Given the inability of Turkey’s strongman Recep Tayyip Erdogan’s to satisfy Turkey’s 86 million citizens with an economy reliant on corrupt patronage networks and the challenges of implementing a heavy austerity program within a democratic framework, diverting public attention to domestic and foreign disturbances to suspend democracy becomes a realistic expectation. Ultimately, Erdogan’s pursuit seems to lead toward a costly Pyrrhic Victory.
By Ibrahim Ozturk
In one of his poems, the late Turkish poet Sezai Karakoc, whose verses were even recited with enthusiasm by Turkish President Recep Tayyip Erdogan, proclaimed, “Never say fate, there is a fate beyond fate,” and spoke of “victories growing from defeat.” Through these words, he sought to nurture the hope that the oppressed, who steadfastly endure in their just “cause,” will ultimately triumph.
Tactical Commitment to Democracy Between 2003-2011
It all began with a “cause”! Erdogan and a few friends decided to engage in politics in an independent party, breaking away from the main political backbone known as National Outlook (Milli Gorus), of which he was a member, and its cult leader, Necmettin Erbakan, in the early 2000s. Erdogan explained his “taking off the National Outlook shirt” as “evolving and transforming towards perfection.” He described Turkey’s fundamental problems as political repression, leading to corruption and resulting in poverty. To break this vicious cycle, Erdogan declared that his team would not address the ambiguous rhetoric of National Outlook but rely on human rights-based, pluralistic, participatory democracy, full membership in the EU and, in this context, a modern and democratic constitution.
The party program of the Justice and Development Party (AKP), which he founded, confirmed this. With the support of EU reforms, favorable domestic and international circumstances, and relatively good governance, he continuously elevated the bar for success during a period that could be considered successful. As a Muslim country on the path to EU membership, adhering to the norms and values of a democratic secular regime and safeguarding the rule of law and a market economy, Turkey stirred feelings of admiration in the Islamic world, underscoring its role model status.
As the famous political historian Lord Acton wrote in a letter to an Anglican priest in 1887, “Power corrupts, and absolute power corrupts absolutely.” Having observed Erdogan’s successive election victories in general elections for central government and local elections for municipalities and his subsequent rise in power, I raised questions in my commentary in Project Syndicate in 2011 about how Erdogan would wield his increasing power or how it would be balanced. The question is legitimate because when populist politicians come to power, they might disregard the promises made to society during their time in opposition. Instead, they may opt to perpetuate the old regime and exploit it for their own benefit rather than reforming it in a positive direction, particularly when confronted with real challenges in governance, leading to the implementation of unrealistic solutions to real problems. Additionally, the manner in which they would relinquish power in case of failure remains a highly controversial issue.
Corruption Economy and Return to Authoritarian Agenda
Much has transpired since then, and the AKP’s utilization of its acquired power has been viewed with dismay. Indeed, following the success of the 2011 elections, Erdogan veered toward a different path. AKP Istanbul Provincial Chairman Aziz Babuscu openly declared at the April 1, 2013, Inner City Meetings what they intended to do: “… in the next decade, we will separate our ways from our stakeholders with whom we collaborated when we were powerless because we will no longer need them. For us, the state and social order they idealized were merely tactics and war ploys. We will depart from this intersection, and due to the bitter realities of life, we will have a callous agenda to eliminate them.”
Therefore, society would come to understand for the first time that the proclamation of being an “exemplary secular-conservative democratic model” before and upon assuming power was merely a strategic maneuver until the AKP cadre consolidated enough power. With the eruption of a corrupt regime, where Erdogan diverted economic resources to construct a political order he had long envisioned, coupled with the environmentalist Gezi Protests in June 2013 and the police-judicial graft operations on December 17-25, 2013, he found himself compelled to expedite the inevitable transition towards authoritarianism. This pivotal juncture, symbolizing the crossing of the Rubicon, is fraught with danger for individuals like Erdogan, burdened by a multitude of transgressions and devoid of any avenue for retreat. Indeed, the die has been cast, the arrow released from the bow, and the conflict has commenced.
We have also witnessed how the evolving multipolar world provides authoritarian populists with additional opportunities to validate their “political engineering” and shift towards more oppressive regimes. By labeling corruption files and probes as “imperialist-foreign capital induced coup attempts against the autonomous government of the people,” Erdogan promptly forged an emergency alliance with the previously corrupt state apparatus inherited in 2002, significantly overhauling it to align with Turkey’s EU membership requisites. In exchange for his cooperation, Erdogan directed his highly politicized judiciary to dismiss all former Gladio-related cases in 2014, thus safeguarding his government and himself while closely collaborating with members of the old oligarchy.
After the defeat in the general elections on June 7, 2015, amidst escalating violence due to a resurgence of intelligence-led terrorism and heightened pressure on the Kurds, Erdogan capitalized on security concerns among the populace. He was subsequently reelected in the snap election held on November 1, 2015. However, achieving his political goals required strategic planning and luck. The “witch hunt,” which couldn’t be conducted within the bounds of a democratic rule of law, found fertile ground only under a state of emergency where legal norms were disregarded. This tactic, often employed by Turkey in the past to target minorities of various ethnic backgrounds, proved effective under such circumstances. The “failed coup attempt” on July 15, 2016, served precisely this purpose.
Following the coup attempt, hundreds of thousands of public employees were dismissed from universities, the judiciary, the police, the military, and the Ministry of Education etc. Dozens of foundation universities, widespread educational institutions, and prep schools were shuttered. Thousands of companies were seized, and their assets confiscated. A witch hunt ensued, wherein people were stigmatized for exercising their constitutional rights, ostracized from society, and rendered unemployable. To solidify Erdogan’s party state, hundreds of thousands of political militants were recruited without regard for merit-based criteria to fill the vacancies left by those purged from the public sector.
With the controversial July 15 coup attempt, not only was the relatively moderate faith-based Gulen movement demonized by Erdogan, but also those who did not support the regime were declared open enemies, or at the very least intimidated, with the slogan “those who are impartial will be eliminated.”
The final stage in the regime’s transformation occurred with the 2017 referendum. The adoption of a partisan Presidential system effectively eradicated the separation of powers and checks and balances. The Turkish Parliament (The Grand National Assembly of Turkey, TBMM) lost its efficacy, becoming a mere formality. The judiciary, police, and media were completely co-opted and utilized to serve the regime’s interests. Authoritarian populism, forsaking long-term scientific and institutional planning in favor of a cult of strong leadership centered around a single man, led to decisions made on a whim and managed arbitrarily. Decisions made overnight were rescinded during the day, while personal preferences and exceptions proliferated. Institutions whose autonomy was dismantled were infiltrated by unqualified party militants.
Several crucial examples illustrate the extent of the damage: the Turkish Statistical Institute’s (TUIK) inability to provide accurate information; the Central Bank of the Republic of Turkey’s (CBRT) inability to execute specialized monetary policies crucial for price stability; the Competition Authority’s inability to prevent market monopolization; and the Banking Regulation and Supervision Agency (BDDK) and the Savings Deposit Insurance Fund’s (TMSF) inability to fulfill their roles in the financial system. Furthermore, the Court of Accounts’ capacity to audit the legality of public administration actions was compromised. The Public Procurement Law underwent constant amendments and violations, leading to inflated costs through preferential tenders, while compromising quality and exacerbating impoverishment. The erosion of the rule of law was further evidenced by the severe repression of civil society.
At this juncture, political power took precedence over social dialogue, exacerbating polarization and conflicts. While certain influential industrialists, pro-government media entities, and rent-seeking groups found favor under the regime, disillusionment grew among the educated middle class and youth, who had once harbored hopes for a society founded on principles of freedom of thought, expression, rule of law, and human rights. The Turkish populace, yearning for an open and progressive society, felt betrayed, particularly evident during the 2017 referendum and the 2018 presidential and parliamentary elections, where they expressed their discontent by voting against Erdogan.
The consolidation of political power within Erdogan’s inner circle, notably through intra-party elections in August 2017 which saw power being transferred to his relatives, and the appointment of his son-in-law as Treasury and Finance Minister in the subsequent government, heightened perceptions of “familism” and cronyism among the public. Projects backed by “customer and foreign currency-indexed price guarantees,” which were later transferred to the Treasury, became significant drains on public finances, resembling black holes in their insatiable consumption of resources.
At this point, it’s crucial to briefly examine Erdoganism’s governing model. Erdogan’s tenure, starting from his days as the mayor of Istanbul, has been characterized by notable successes in creating “win-win games” and “interest coalitions” primarily through rent-seeking. In this corrupt system, Erdogan has enriched himself through a give-and-take approach. Secondly, “purchased loyalty” emerges as another key aspect. His transactional strategy involves incentivizing individuals to partake in his corrupt regime by generously sharing the spoils, thereby securing their loyalty, and inducing compliance. Thirdly, a tactic of creating scapegoats and governing through division, even if it means ruthlessly sacrificing one’s allies and offspring when necessary. For Erdogan, any means to achieve his objectives are deemed permissible. Politics is regarded as a battlefield, where deceit and stratagems are not only necessary but also legitimate. This ethos shapes both alliances and enmities. Just as forming coalitions is inevitable, so too is the elimination of partners to strengthen one’s position at every stage.
Tragedy of Patronage in A Low Productivity Economy
Despite the exposure of Erdogan’s blatant corruption model during the December 17-25, 2013 corruption operations, the public did not retract its support from this political structure, which it perceives as vital to its bread and freedom. As is the case globally, the political behavior of Turkish society oscillates between instability, fear of authority, and the risk to livelihood. Until the adverse effects of the deeply entrenched corruption within the regime directly impacted their lives, society not only refrained from reacting out of fear that Erdogan’s absence could lead to instability, but also remained steadfast in their support for him.
Numerous factors, including justice, contribute to the source of political legitimacy, yet the provision of livelihood stands out as the pivotal influence. Erdogan’s dilemma lies in maintaining the sustainability of a patrimonial order characterized by high levels of contingency and arbitrariness in a country as populous as Turkey, with its 86 million inhabitants, largely possessing relatively weaker human capital. Furthermore, the challenges posed by the country’s large population and the inadequacy of natural resources are compounded by external changes. As the world undergoes a new wave of “creative destruction” marked by intensified technological competition, driven by the Fourth Industrial Revolution and the Fifth Generation Communication Revolution, Erdogan’s focus on sectors from the first and second industrial revolutions, such as textiles and land-construction, which are shielded from foreign trade and competition, as well as rent-seeking activities facilitating wealth transfer, proves unsustainable.
Attempting to evade the Middle-Income Trap (MIT) through reliance on these sectors—often associated with the lowest value-added and situated at the cheapest end of the global value chain—is futile. The MIT concept posits that traditional sectors, at the current stage of development, are excessively costly to compete with low-cost developing countries, while modern sectors demand higher quality and added value to rival leading industrialized nations. Consequently, the manufacturing industry finds itself trapped between traditional sectors characterized by high prices and modern sectors marked by inadequate quality.
Indeed, in a 2012 economic report I edited for the Independent Industrialists and Businessmen’s Association (MUSIAD), of which Erdogan was one of the founders, I forecasted a continuous decline in per capita income from 2013 onwards, suggesting that Turkey would likely fall into the MIT by the 100th anniversary of the Republic. These projections have largely materialized today: Per capita income, which stood at $12,500 in 2013 and for the first time in her modern history put Turkey on the brink of entering the high-income country group and attracting global attention, has steadily decreased and plummeted to $10,674 by 2022. In the context of the 2023 election, due to excessive suppression of the exchange rate and the exclusion of migrants, who were considered in the calculation of the gross domestic production (GDP), when GDP was divided by the population, per capita GDP was reported as $13,000 (Figure 1). Despite the national income remaining at $1 trillion in 2023, the per capita income aimed at $25,000 stagnated at half that level—a loss of a decade’s worth of progress. Turkey, which climbed to the top of the developing country groups in the 2012-2013 transition, has slipped back to the status that Erdogan took over 20 years ago, as of 2022. In 2021, Turkey dropped out of the “top 20 largest economies in the world” rankings for the first time in modern history.
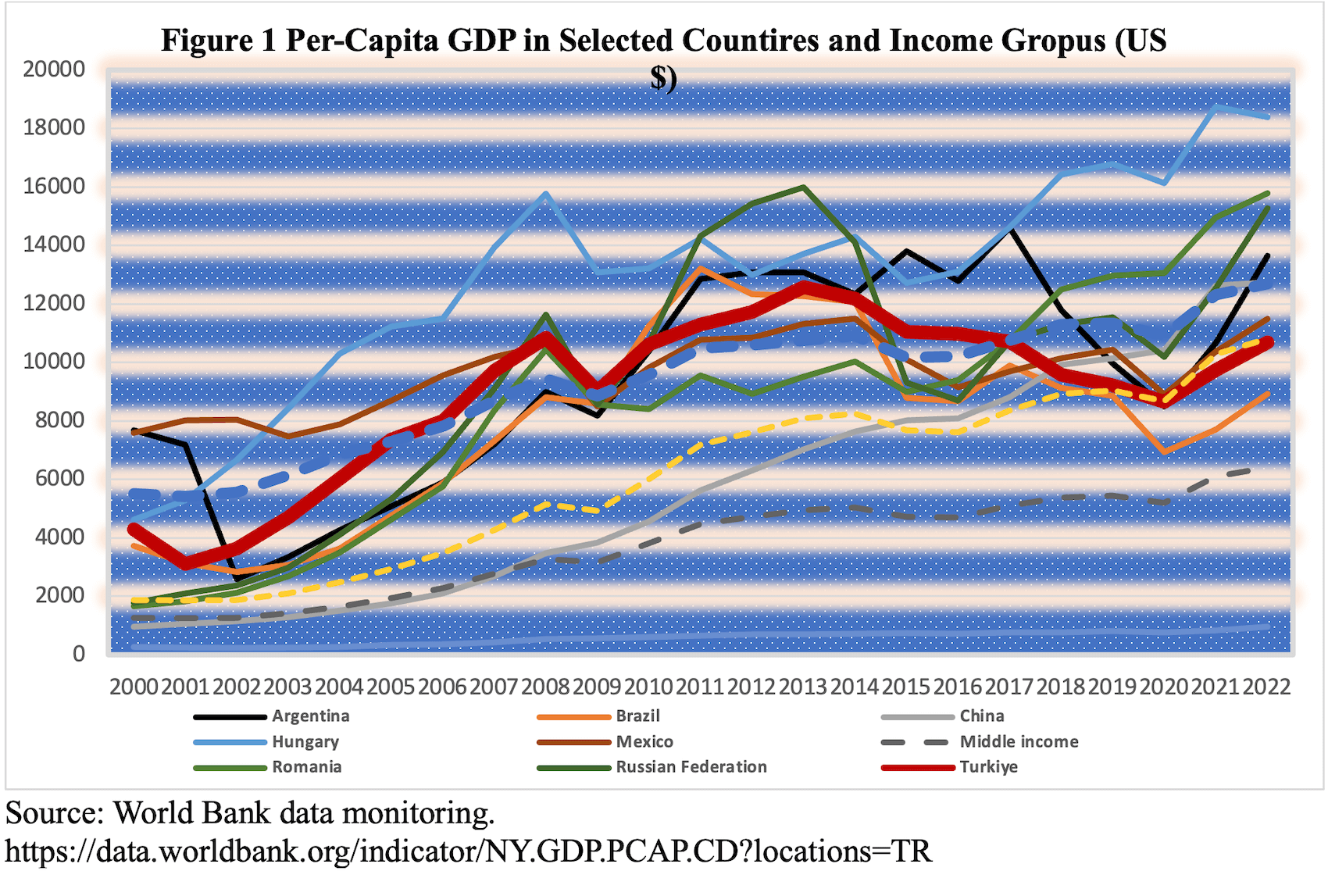
The predictions regarding macroeconomic management under populist regimes, spanning from right to left-wing populists, have been largely confirmed in Erdogan’s case. Initially, Erdogan began his term in late 2002 with an IMF program and effectively implemented EU reforms. However, following the regime change in 2018, which marked the onset of his authoritarian tendencies, Erdogan exhibited numerous shortcomings. These included the implementation of expansive monetary and fiscal policies, resulting in soaring inflation rates, price controls, credit rationing, persistent budget deficits, unsustainable debt accumulation, arbitrary and short-term decision-making, non-compliance with established economic programs, and failure to achieve projected outcomes.
Erdogan’s management has failed to address chronic macroeconomic imbalances, characterized by persistent external and internal deficits, high inflation rates, volatile borrowing and lending rates, and depreciation of the Turkish Lira (TL), thus impeding the economy from achieving sustainable growth. The economic environment, marked by a sharp annual increase in broad money supply by 65 percent and the political decision to keep the policy rate well below inflation, has led to a significant negative real return, creating conditions favorable to speculative attacks on the TL. Heightened insecurity and uncertainty have further increased demand for foreign exchange, while the annual credit volume has surged by approximately 55 percent, driving up consumption and import demand and inflating the real estate sector bubble. These factors have exacerbated inflationary pressures, which have already spiraled out of control (Figure 2a). Johns Hopkins University professor Steve H. Hanke and the Inflation Research Group (ENAG) have meticulously uncovered a stark reality: TURKSTAT, evidently under the direct influence of Erdogan’s administration, has significantly understated inflation data. This revelation sheds light on a deliberate manipulation aimed at distorting income distribution, particularly impacting fixed-income civil servants, workers, and employees. The wealth transfer orchestrated through this misrepresentation has inflicted a substantial blow to their financial well-being (Figure 2a).
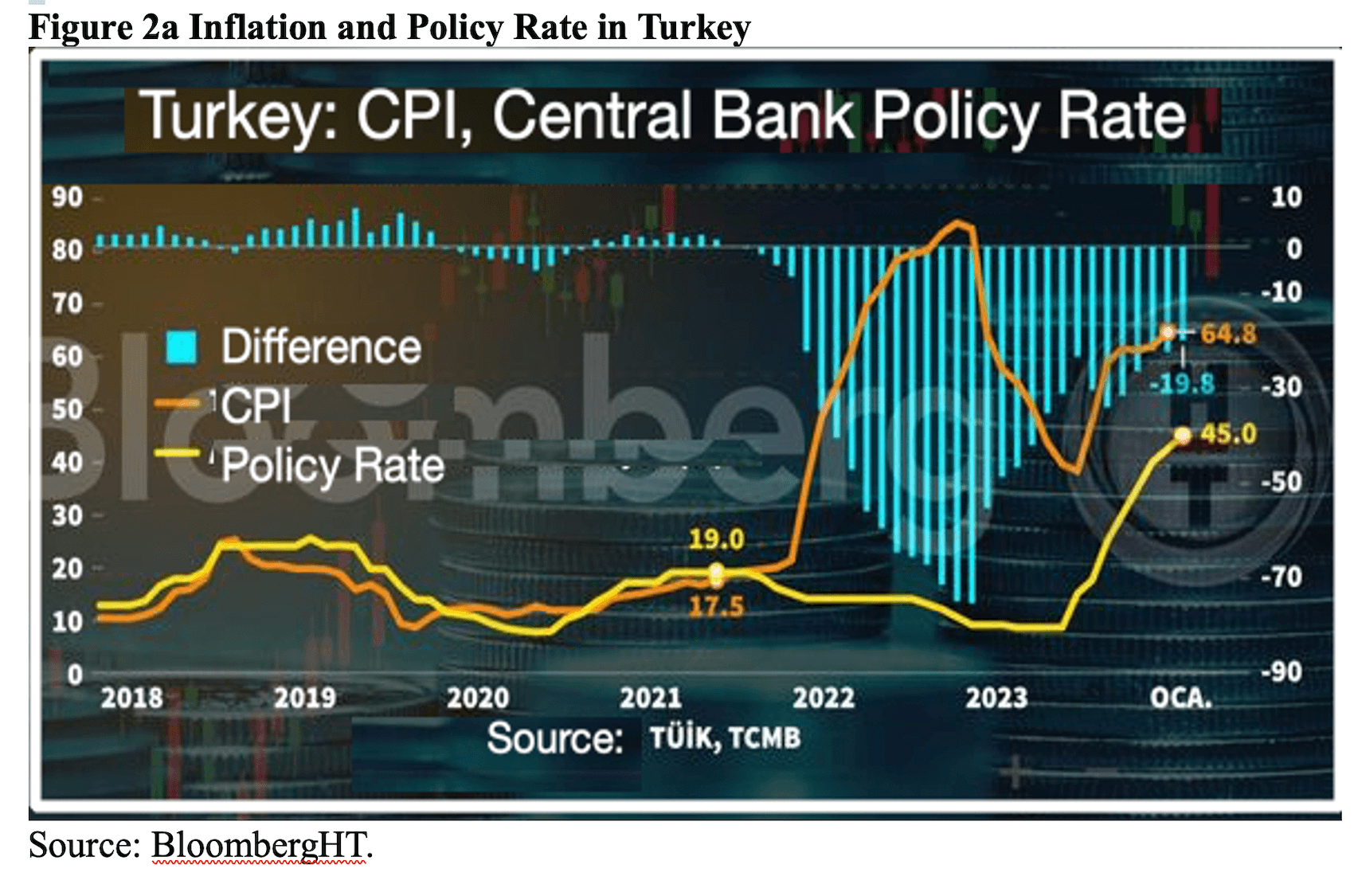
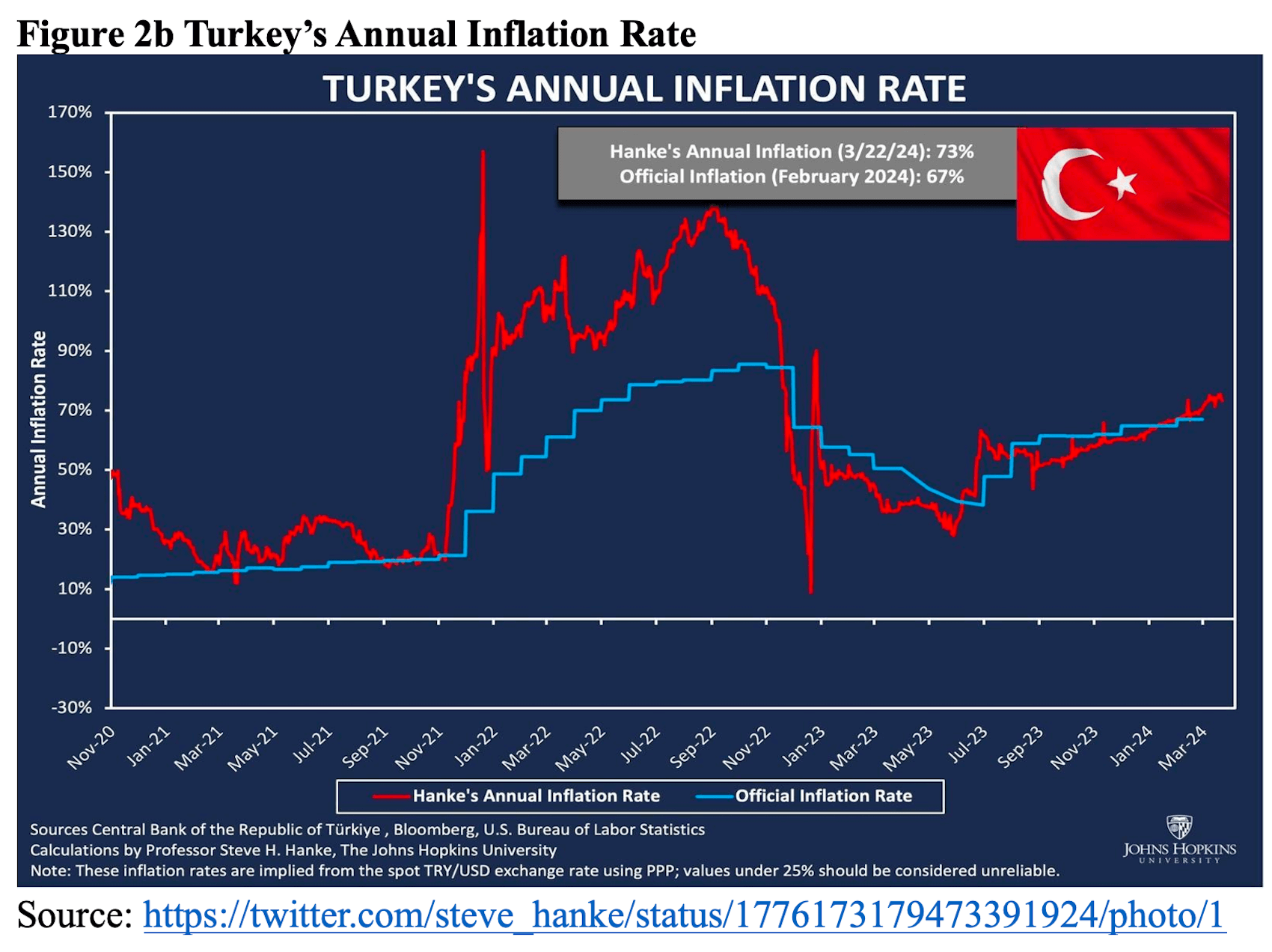
Meanwhile, the dollar exchange rate surged from ₺3.86 in 2018, the year of the regime change, to ₺32 by the end of March 2024, marking an 850% depreciation of the TL over five consecutive years. Despite unreliable public data, inflation spiked to around 100% at one point in 2022, up from 17% in 2020, before closing the year at 65%. The same level of inflation, 65%, was recorded in the election year 2023. However, Erdogan intervened aggressively in the foreign exchange markets to curb further inflation after his politically motivated decision to lower interest rates, depleting over $200 billion from central bank reserves in just two years.
With Mehmet Simsek’s return to politics, who served as finance minister in the AKP government until 2018, in June 2023, and his reappointment to the same ministry, there has been discussion of a stabilization program under the motto “cutting off the wrong and returning to rational ground.” However, despite having a name, its content has remained unfulfilled. When Simsek took office, the CBRT policy rate stood at 8.5%, with inflation around 39%. By the end of 2023, the interest rate had soared to 45%, while inflation reached 65% by the year’s close. Despite selling more than 40 billion dollars of additional borrowed reserves from the Central Bank, and the interest rates rose to 50% during the election to repress inflation, it hit 68,50%. Such a doubling of consumer inflation over less than a year, accompanied by an almost 6 to 7-fold increase in the policy rate, is highly unusual, reflecting the heavy injury of the demand and supply mechanism. Populist policies implemented following successive elections have worsened expectations, and the secondary effects of the inflation shock in autumn 2021 appear to be further strengthening.
Erdogan’s “economic model,” based on unfulfilling prophecies and aimed to determine the opportunity cost of money through political decrees centrally, assumed that lowering interest rates would reduce production costs and decrease inflation. It also posited that an increase in the exchange rate would enhance Turkey’s export competitiveness, thus allowing the country to close its foreign exchange deficit. However, these prophecies did not come true, and instead, the opposite happened. The model eventually transitioned into a tragic stage when Erdogan and his “politburo members” attempted to control inflation through direct and indirect exchange rate and price controls at all costs. This “learning-by-doing experience,” which incurred a devastating political and economic cost, reflects the tragic “self-fulfilling prophecies” of populist leaders like Erdogan, who aim to keep interest rates low while unreasonably hoping to prevent prices, foreign exchange rates, and inflation from rising. The process resulted in an incredible transfer of wealth and increased cost of living in favor of a small segment of society at the expense of the majority.
As outlined above, the challenges under Erdogan’s regime extend beyond resource allocation efficiency and raise significant concerns about distributional issues. This is sadly reflected in Turkey’s income and wealth distribution statistics in 2023, compiled by TUIK. According to labor union studies conducted in March 2024, the hunger threshold for a family of four in Turkey, where the minimum wage is 17,000 TL, was estimated at nearly 20,000 TL, while the poverty line stood at almost 55,000 TL. Thus, voters faced dire circumstances without security or other guarantees when hunger and poverty levels reached such heights. According to TUİK, by 2023, the share of the highest-income group, comprising 20 percent of the population, had surged to 50 percent of the national income, while the lowest-income group remained stagnant at 6%.
The Gini coefficient, a key measure of income inequality (where zero indicates perfect equality and one signals extreme inequality), has been on the rise since 2014, reaching an estimated 0.433. Finally, data released by Credit Suisse and UBS in March 2024 depict an even grimmer picture of wealth distribution in Turkey. The country’s wealth Gini coefficient stands at 0.8, with the wealthiest 10% owning a staggering 70%. According to a recent European Commission for Turkey report, Turkey still lacks a dedicated poverty reduction strategy. After sustained price increases, the poverty rate reached 14.4%, up from 13.8% in 2021. The severe-material-deprivation rate reached 28.4% in 2022.
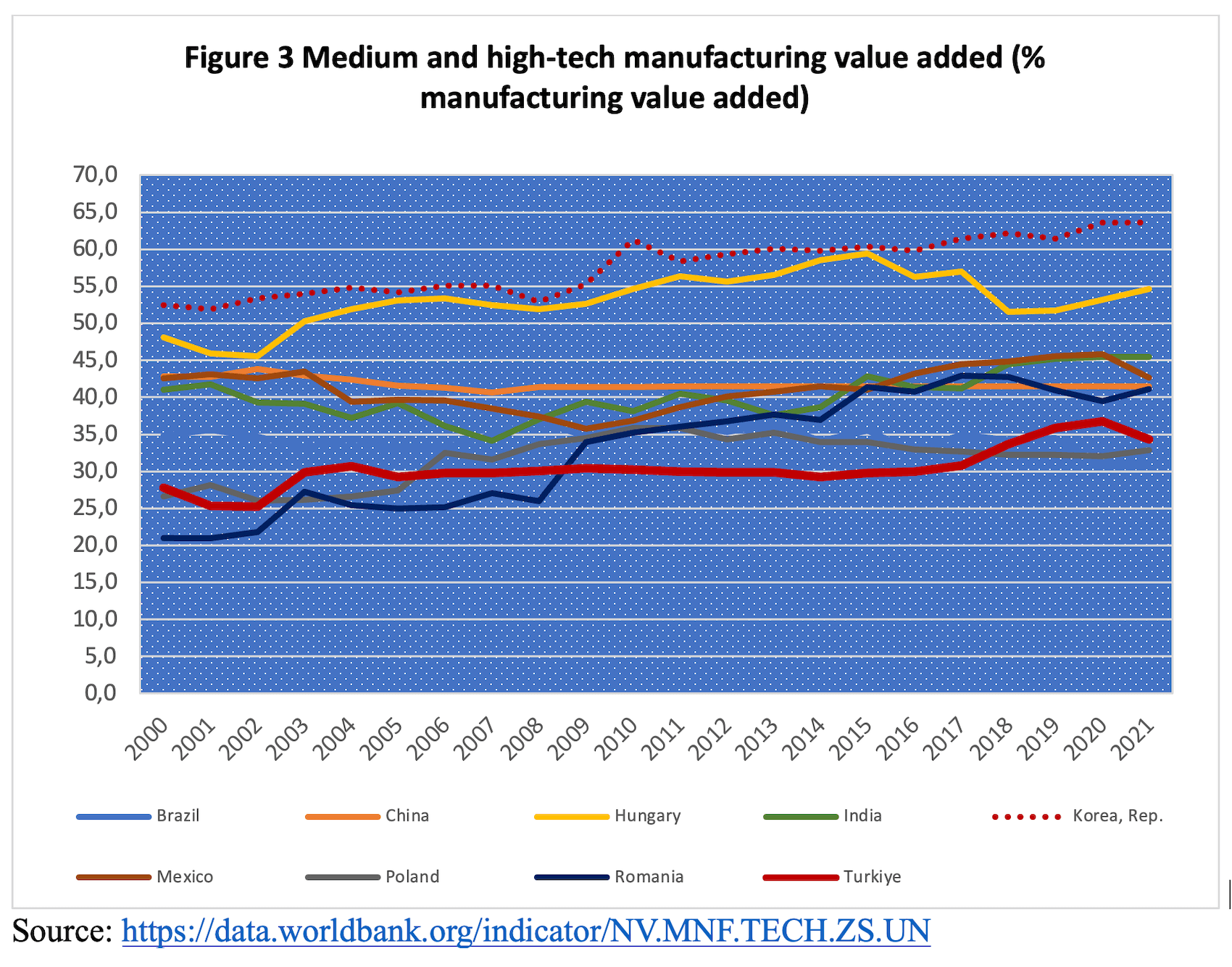
In that, after 2011, it became increasingly evident that Erdogan’s focus shifted towards exploiting the flaws of the old regime to consolidate his government rather than addressing political repression, corruption, and poverty. Instead of actively tackling poverty and income inequality, he opted to “manage” these issues, perpetuating a cycle of dependency. Emerging data summarized above shows that Erdogan can not sustain his role as a Robin Hood figure, redistributing part of the wealth generated from public rents to society through various mechanisms in a low-value-added, low-productivity economy (Figure 3) with a population of 86 million people.
A recent publication indicates that this range of patronage or patrimonial economic relationships was facilitated through cultural and ideological narratives, civilizational and religious populism, anti-elite polarization, and the government’s inclination to scapegoat foreigners.
Erdogan’s purported model, as discussed thus far, aims to position Turkey as a “cheap production base” in the western part of Eurasia and the eastern part of Europe by suppressing real wages, utilizing cheap surplus labor provided also by immigrant workers, channeling people’s savings to cronies through subsidized interest rates, attracting capital by devaluing all national assets through currency depreciation, sustaining economic growth inflated by inflation, raising indirect taxes, and ultimately exporting low-value-added products to improve the external balance. However, these objectives have yet to be fully realized. Despite the sharp devaluation of the TL and the imposition of very high customs duties, trade deficits have continued to increase, and financing quality has deteriorated, leading to the accumulation of unsustainable foreign debt (Figures 4 and 5).
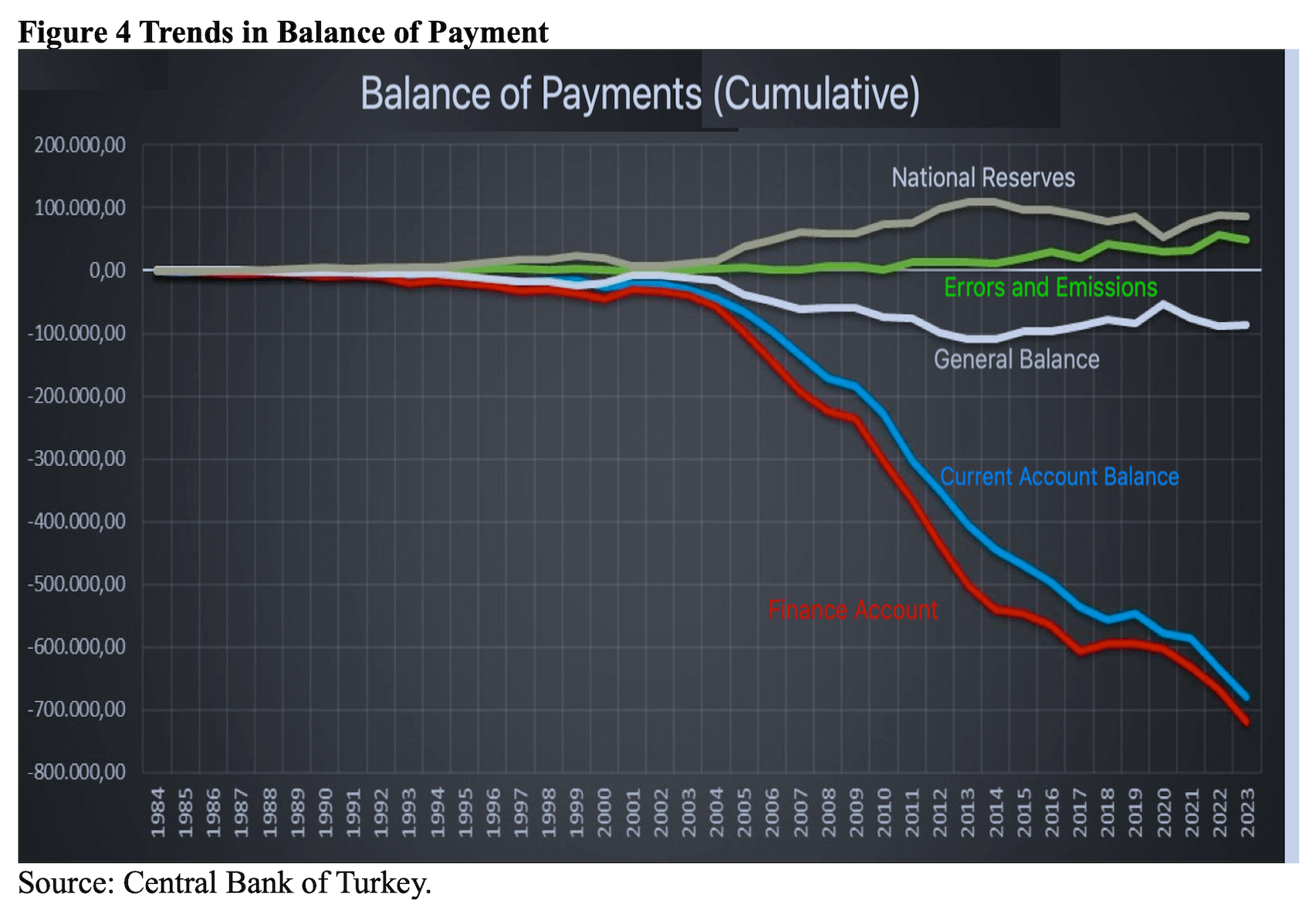
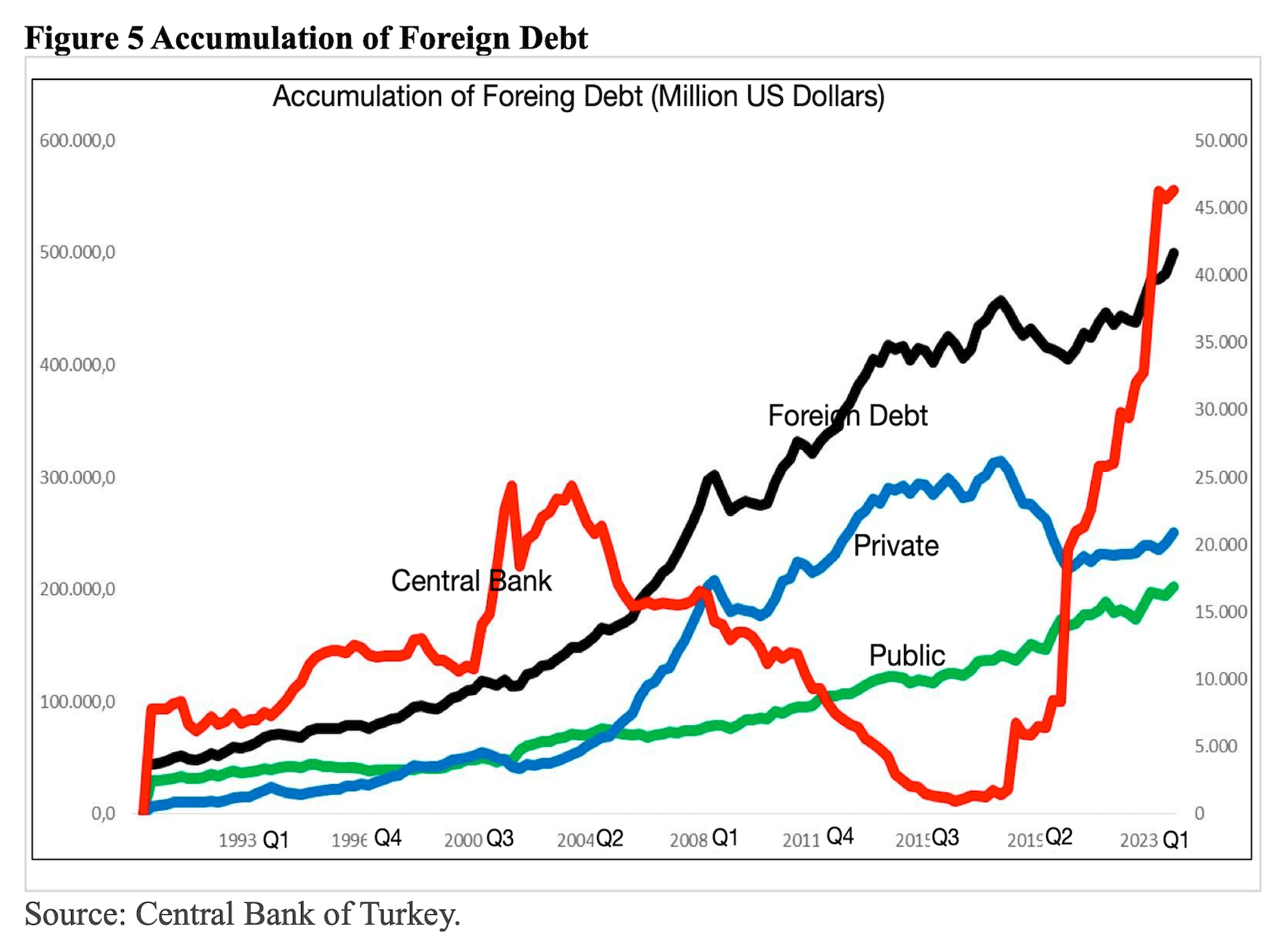
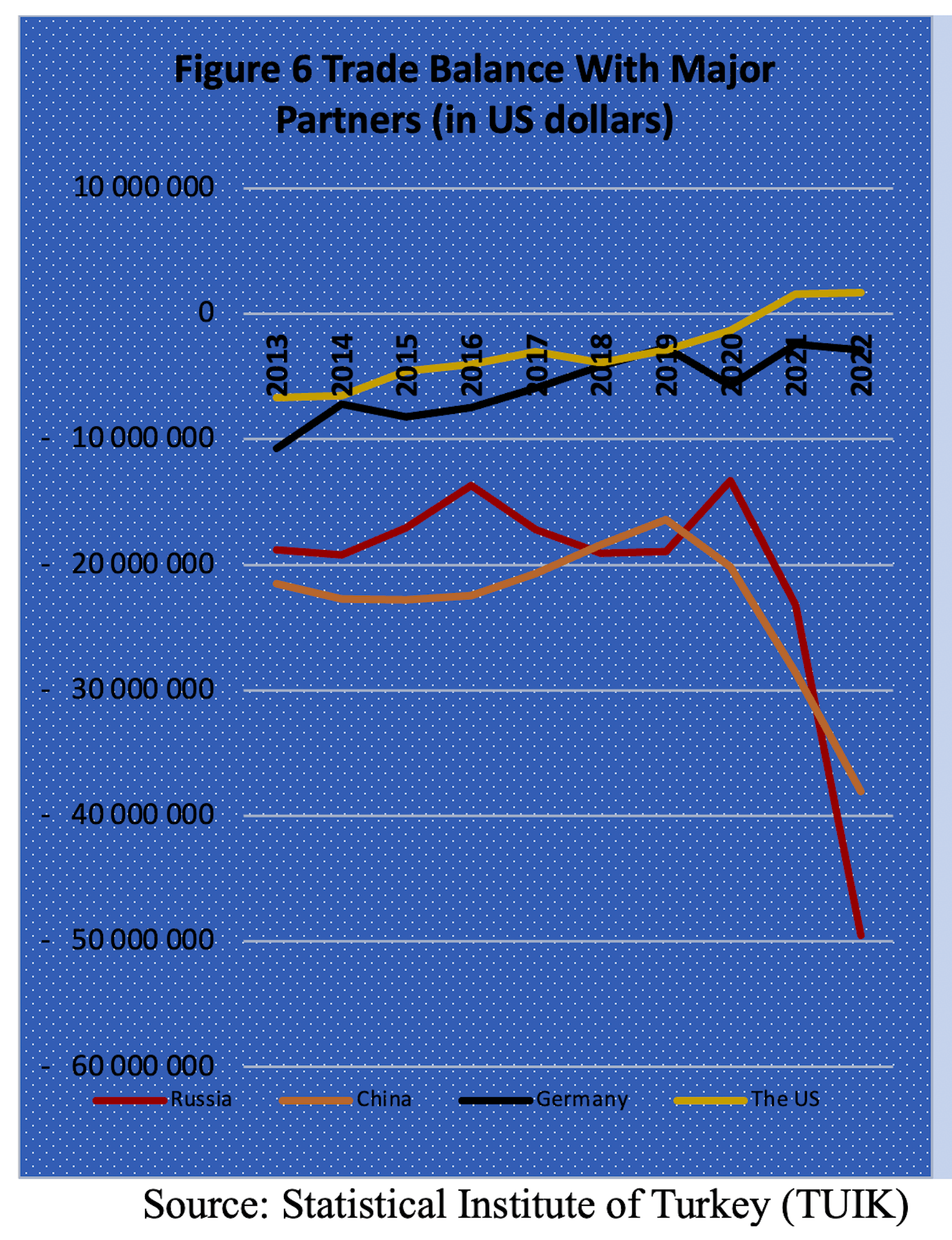
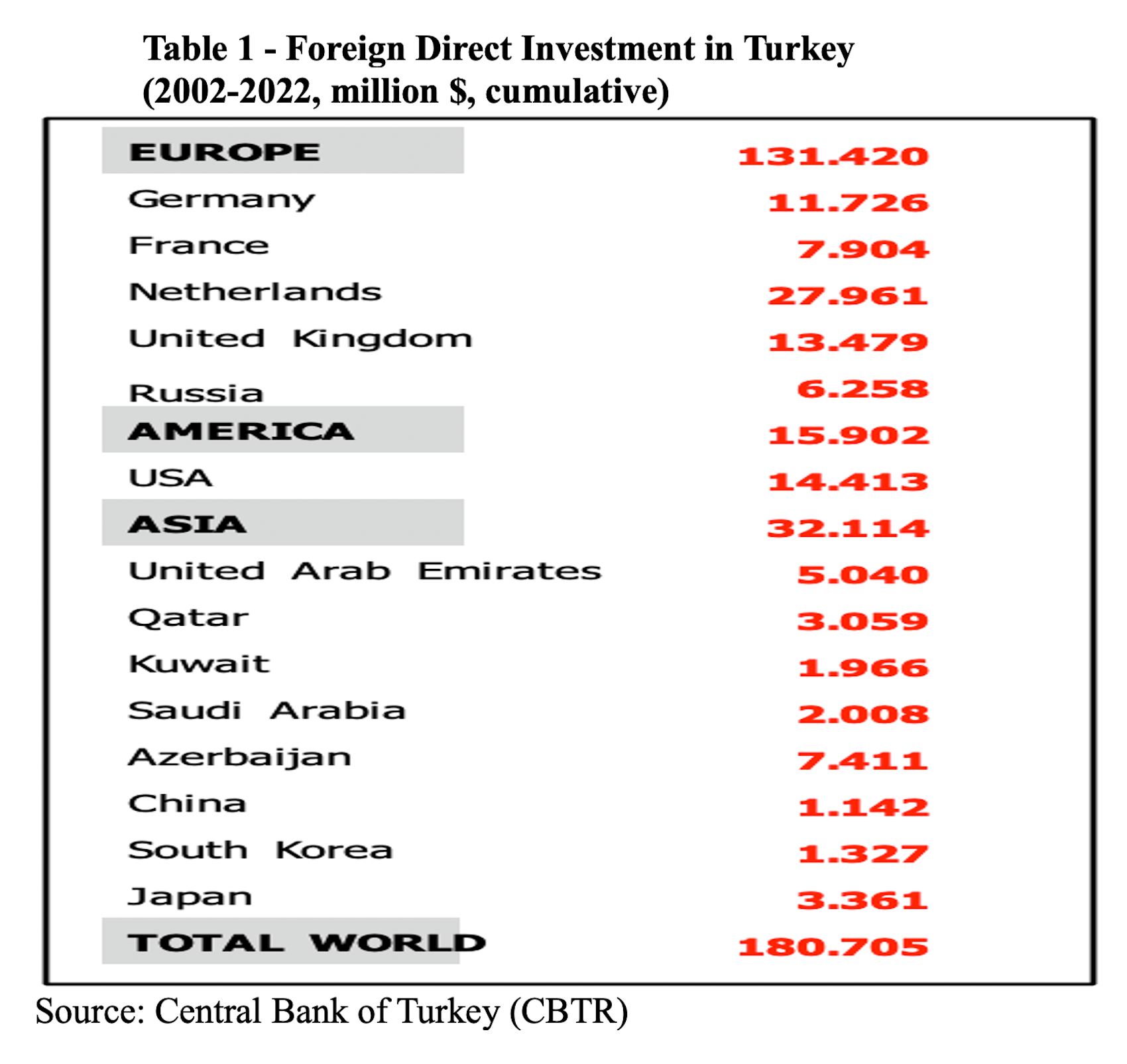
From a longer-term perspective, the combined impact of institutional erosion, the dismantling of checks and balances, and a contentious foreign policy under autocratic rule have resulted in flawed economic policies and the disintegration of the production fabric. The total volume of Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) entering Turkey has experienced a sharp decline since 2007. The crisis of trust has led Turkey to detach from the European value chain. Simultaneously, political tensions with major Arab countries like Saudi Arabia and Egypt have prompted a distancing from the Middle Eastern market. Meanwhile, Erdogan’s allies in Eurasia, such as China and Russia, dominate in trade deficits but do not contribute to financing. China relegates Turkey to merely an “open market” and a “transit route” to access the EU and neighboring countries duty-free. In summary, China and Russia are the primary sources of Turkey’s trade deficit, while the source of finance remains traditionally Western Europe (Figure 6, Table 1).
‘God of Hunger’ Prevails over the “Gods of Fear’
In Greek mythology, Limos represents the embodiment of starvation, hunger, and famine, while Deimos and Phobos epitomize chaos and fear. Deimos symbolizes terror and dread in ancient Greek religious beliefs and mythology, whereas his sibling Phobos embodies panic, flight, and rout. Recently, the Turkish populace, losing hope and experiencing escalating hunger, has rebelled against the dominion of the “gods of fear.” Instead, they find themselves under the sway of the god of hunger, embodying their current struggles.
In the March 2024 local elections, amid the economic crisis and regional and global contractions in foreign policy, a pivotal moment emerged where the “god of hunger” prevailed over the “god of fear.” Despite the government’s extensive propaganda urging the populace to prioritize “stability,” maintain “gains” under Erdogan’s regime, and resist foreign influence, people turned a deaf ear to these messages. Consequently, the elections resulted in a resounding defeat for the ruling party.
In recent years, Erdogan has crafted his entire political narrative around themes of national honor, sovereigntism, independence, and autonomous foreign policy. Consequently, he has leaned towards polarization, alienation, and divisive governance both domestically and internationally. Erdogan has positioned himself as the guardian of the Muslim ummah, the champion of a Free Palestine, and the rightful inheritor of former Ottoman territories. However, his loss of ability to engage in economic and political populism at home and abroad during the March 2024 local elections underscores the unsustainability of populism in a country of Turkey’s magnitude and geopolitical complexity. It is indeed a notable irony in the history of a religiously motivated populist authoritarian political leader to transition from the rhetoric of the “caliphate of the ummah” to being labeled as a “collaborator of Zionism” amid Israel’s Gaza massacres. This shift arises from the diverse forms of support, including weapons and kerosene, extended to the Netanyahu government during the ongoing massacre of civilians in Gaza and the relentless destruction of the city. This transformation must be viewed as a profound turn of events in the history of the region.
Finally, despite the ruling party’s defeat in the local elections, the opposition strategically positioned itself to claim victory. Firstly, by gaining control of critical municipalities in major cities through the “Nation Alliance,” formed in 2019 as a counterforce to Erdogan’s “People’s Alliance,” the opposition effectively deprived the government of a populist tool while providing an avenue for engagement with the public and showcasing its capabilities. Despite Erdogan’s acknowledgment that losing Istanbul equated to losing Turkey, he couldn’t prevent it in 2019. Fast forward to 2024, not only did he fail to reclaim any major cities lost in 2019, but the losses extended further, with additional significant cities slipping away.
Utilizing this opportunity, opposition-led municipalities efficiently reached out to citizens facing hardships during the crisis. Secondly, the opposition embraced positive populism, taking cues from Erdogan’s playbook. This involved a notable transformation within the main opposition party, the Republican People’s Party (CHP), which shifted from its elitist and establishment image to a more grassroots approach. By speaking the language of the people, acknowledging past shortcomings, and seeking forgiveness, the CHP significantly bolstered its appeal and credibility among the populace.
Conclusion
Following Erdogan’s recent electoral defeat, exacerbated financial crisis, and foreign policy constraints, the period between 2024 and 2028 is poised for turbulent developments. The stark contrast between the people’s needs and Erdogan’s priorities renders the situation even more fragile. Erdogan’s primary objective is to maintain power and evade accountability at all costs.
The inevitable repercussions of the March 2024 local elections seem unavoidable, primarily due to the substantial number and size of municipalities lost, rather than merely the overall voting percentages. These cities predominantly housed Erdogan’s rent projects, thrived on corrupt economies, and relied on assistance to people experiencing poverty, cementing their dependence on him.
Hence, Erdogan suffered losses not only in terms of the popular vote but also in terms of financial resources. Ambitious projects like “Canal Istanbul” or the construction of malls in Taksim Gezi Park now seem unattainable. Moreover, his loss of domestic support and resources has tarnished his reputation. To reclaim these lost assets, it’s foreseeable that Erdogan will centralize numerous resources and administrative units previously overseen by municipalities. This might involve appointing trustees to many cities, obstructing municipal budgets, and hindering investment financing initiated by municipalities.
However, instead of focusing on trivial matters, a more comprehensive political strategy should be anticipated to address the underlying issues. The saying goes, “each blow that doesn’t kill strengthens.” Erdogan finds himself wounded, vulnerable, and, consequently, highly perilous. Just as Turkey spiraled into a state of fear following the June 7, 2015 elections that he lost and witnessed the suspension of law after the failed coup attempt orchestrated by government intelligence on July 15, 2016, Erdogan might resort to provoking Kurds and stoking societal tensions using his concocted “FETO” narrative to neutralize the impact of local elections by sidelining legal procedures once more.
The recent attempt to hinder the elected candidate in Van province immediately after the election may signify something more than a conclusion but rather the inception of a more extensive process. Erdogan’s alliance with the ultranationalist National Action Party (MHP) and its leader, Devlet Bahceli, known for their connections with criminal elements, could potentially draw Erdogan into hazardous undertakings, leveraging Turkey’s instabilities to their advantage.
Another urgent agenda that influences the aforementioned projects is Turkey’s austerity program, whether implemented with or without the IMF. Turkey is currently facing economic and political crises, and implementing a rigorous stabilization program is crucial to mitigate inflation and urgently address the foreign exchange shortage. However, the societal burden of such programs is significant, and only a newly elected government with high credibility could realistically enact one. Given the ongoing erosion of trust, compounded by Erdogan’s autocratic regime’s arbitrary and amateurish practices, it seems unlikely that the current government could effectively execute such a demanding program to fully address the situation.
The upbeat “signaling effect” of an IMF agreement is undoubtedly more urgent than a gradual loan dispersal. Yet, Erdogan’s acceptance of such an agreement presents another challenge, as it would require substantial reforms, including transparency, accountability, addressing past crimes, and moving away from entrenched corruption. Moreover, the specific political and economic concessions the US might demand from Turkey to facilitate an IMF agreement still need to be determined.
In terms of the root cause of Erdogan’s tragedy in Turkey, while Erdogan endeavors to assert leadership within “the Islamic Ummah” rather than “bowing to Europe,” he finds himself increasingly isolated not only from Europe but also from the Arab world. His efforts to appease Russia and China have faltered, and he is entangled in a costly “war of liberation” without sufficient resources. In this scenario, the longstanding propaganda that portrayed Erdogan as “the guardian of the Ummah” has collapsed and been replaced by the perception of him as a “Zionist collaborator.”
Therefore, given Erdogan’s inability to satisfy Turkey’s 86 million citizens with an economy reliant on corrupt patronage networks and the challenges of implementing a heavy austerity program within a democratic framework, diverting public attention to domestic and foreign disturbances to suspend democracy becomes a realistic expectation. Ultimately, Erdogan’s pursuit appears to lead toward a costly Pyrrhic Victory.


















