Please cite as:
Ozturk, Ibrahim & Fritsch, Claudia. (2025). “Discursive Violence and Moral Repair: The Promise and Limits of Non-Violent Communication Against Populism.” Populism & Politics (P&P). European Center for Populism Studies (ECPS). November 19, 2025. https://doi.org/10.55271/pp0051
Abstract
Marking the hundredth anniversary of fascism’s rise in Europe, this article explores the recent resurgence of authoritarian populism—now deeply embedded within democracies and intensified by digital technologies. It investigates how populist actors use emotionally manipulative and polarizing rhetoric, especially on social media, to diminish empathy, increase affective polarization, and weaken public discourse. Using Marshall Rosenberg’s Nonviolent Communication (NVC) framework, we see populist messaging as a form of discursive violence rooted in blame, moral absolutism, and dehumanization. Conversely, NVC offers a principled way of communicating based on observation, emotional awareness, shared human needs, and compassionate dialogue. Drawing on insights from political communication, discourse analysis, and moral psychology—including moral foundations theory and digital polarization studies—the article examines NVC’s potential as both an interpretive tool and a dialogical intervention. It also discusses important limitations of NVC in adversarial digital environments, such as asymmetrical intent, scalability issues, and the risk of moral equivocation. Ultimately, the article advocates for NVC-informed strategies to restore respectful, empathetic, and authentic free expression amid rising populist manipulation.
Keywords: Authoritarian Populism, Discursive Violence, Emotional Manipulation, Affective Polarization, Nonviolent Communication (NVC), Compassionate Dialogue, Moral Foundations Theory, Digital Polarization, Dehumanization, Moral Equivocation, Scalability Challenge
By Ibrahim Ozturk & Claudia Fritsch*
Introduction
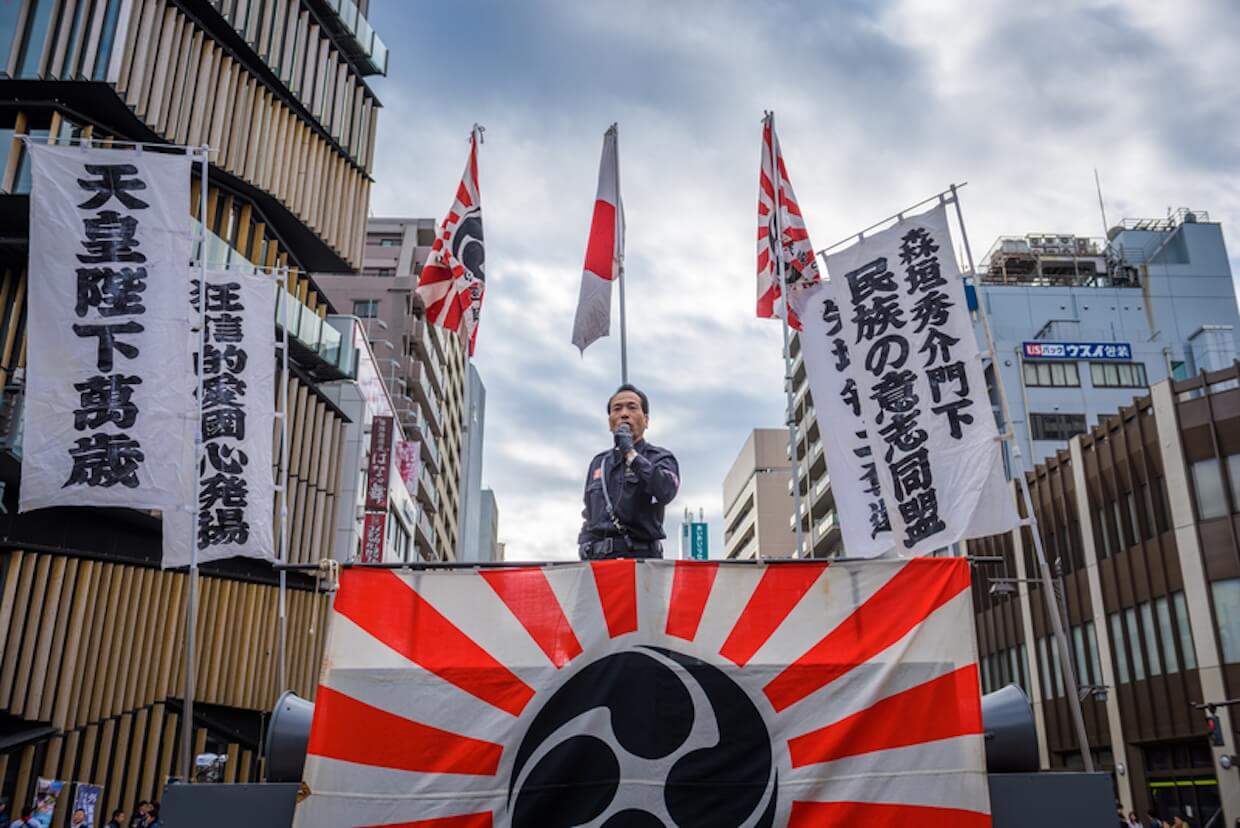
Populist political movements have surged in recent years, characterized by a style of communication that many observers deem manipulative, polarizing, and emotionally charged. Populist rhetoric typically divides society into a virtuous “people” and a corrupt “elite,” conveying simplistic, us-versus-them narratives while often scapegoating minority groups or outsiders (Engesser et al., 2017). Messages from populist leaders are usually delivered in stark, moralistic terms (e.g., “with us or against us”) and strategically tap into emotions such as anger, fear, and resentment to mobilize support. Indeed, scholars note that populist discourse often employs a “manipulation strategy” that exploits emotions to the detriment of rational political considerations (Charaudeau, 2009). This is especially evident on social media, where algorithm-driven amplification rewards sensational and emotionally charged content, providing populist communicators with an ideal channel to disseminate their messages unfiltered. These trends challenge democratic discourse: How can society counter manipulative and divisive communication without resorting to censorship, instead fostering genuine and constructive dialogue?
This article examines Marshall Rosenberg’s framework of Nonviolent Communication (NVC) as a potential remedy to populist, manipulative discourse. NVC, rooted in principles of empathy, honest expression, and mutual understanding, provides a communication model that starkly contrasts with the populist approach of emotional manipulation and scapegoating. By analyzing insights from political communication, critical discourse analysis, psychology, and digital media studies, we will explain how populist strategies operate on social media and how Rosenberg’s NVC might help protect public discourse against them. We include empirical findings, such as studies of Twitter and Facebook rhetoric, to demonstrate populism’s emotional and divisive tactics. We also explore related psychological theories—from moral foundations to affective polarization—to strengthen the theoretical foundation. Furthermore, we address the limitations and critiques of applying NVC in the complex online populism landscape, including concerns about scalability, bad-faith actors, and the potential for moral neutrality. Ultimately, the aim is to promote a “truly free expression” online—not in the sense of unchecked abuse or propaganda, but a space where citizens can engage honestly without fear, manipulation, or dehumanization—an environment NVC strives to foster.
The article is organized as follows. Section 2 establishes the theoretical framework, beginning with an analysis of populist communication in the digital age and its emotionally manipulative strategies, followed by an in-depth discussion of Marshall Rosenberg’s Nonviolent Communication (NVC) model and its foundational principles, and concluding with relevant psychological theories that explain the emotional and moral mechanisms underlying populist appeal, as well as the potential of NVC to address them. Section 3 synthesizes these insights to evaluate how NVC might serve as a discursive counterstrategy to populist manipulation, particularly in online contexts. Section 4 then critically examines the practical challenges and limitations of applying NVC against populist rhetoric, including issues of scalability, asymmetric intent, moral ambiguity, and evidentiary support. Finally, Section 5 concludes by reflecting on the promise and limits of NVC as a communicative antidote to rising authoritarian populism, while offering directions for future research, policy, and civic engagement.
Theoretical Framework
Populist Communication in the Digital Age: Manipulative Strategies and Emotional Appeals
Liberal democracy is facing legitimacy problems due to post-politics, post-democracy, and post-truth dynamics. Populism exploits emotional deficits and distrust in institutions, while digital media amplify fragmentation and emotional escalation (Schenk, 2024). Democracy generates emotional deficits such as individualism and isolation, which foster the rise of “soft despotism” (Helfritzsch & Müller Hipper, 2024). Populist actors exploit these emotional deficits—such as frustration, fear, and mistrust—for mobilization.
Populism is often seen as a thin-centered ideology or style that pits “the pure people” against “the corrupt elite,” arguing that politics should prioritize the will of ordinary people above all else (Engesser et al., 2017). While populist movements exist across the political spectrum, their communication styles tend to follow common patterns. Research in political communication and discourse analysis reveals that populist actors tend to favor simple, colloquial language and binary framing over nuanced expressions (Engesser et al., 2017). Complex issues are often reduced to black-and-white narratives – for example, “you are either with us or part of the problem” – which reinforces in-group/out-group divisions. This kind of dichotomous framing is further supported by frequent use of stereotypes and sometimes vulgar or insulting language aimed at perceived “enemies,” all to dramatize the threat posed by “the elite” or out-groups. Critical discourse analysts observe that this mode of communication intentionally dehumanizes opponents and criminalizes certain groups, rallying the base while dismissing dissenting voices as illegitimate or evil.
A key feature of populist communication is its emotional strength. Populist leaders intentionally appeal to negative feelings—especially fear, anger, and resentment—to rally support and direct public anger toward specific targets. For example, a content analysis of thousands of Twitter messages by European populist parties found that “fear, uncertainty, or resentment are the emotions most frequently used” by these actors (Alonso-Muñoz & Casero-Ripollés, 2023). In those social media messages, negative emotional language (expressing threat, crisis, outrage) was closely linked to references to out-groups or “corrupt authorities,” while positive emotions (such as pride or hope) were generally reserved for the in-group—celebrating “the people” or portraying the populist leader as the savior (Alonso-Muñoz & Casero-Ripollés, 2023). This supports comparative research that suggests populists intentionally stir public anger and fear to rally their supporters. By emphasizing a sense of crisis and victimhood (e.g., depicting society as on the verge of collapse or “invaded” by outsiders), populist rhetoric creates a sense of urgency and danger where extreme actions seem justified. Charaudeau (2009) noted that populist discourse “plays with emotions to the detriment of political reason,” appealing to visceral feelings rather than critical thinking.
The rise of social media has intensified these manipulative techniques. Digital platforms like Twitter and Facebook allow populist politicians to bypass traditional media gatekeepers and connect directly with audiences. In this context, Pörksen (2018) speaks of a weakening of traditional gatekeepers (e.g., journalists) in favor of invisible agents of information filtering and distribution (Pörksen, 2018: 71). Studies show that populists eagerly utilize the features of social media for unfiltered self-promotion and aggressive opposition against opponents (Engesser et al., 2017). They control the online narrative by constantly pumping out simple, emotionally charged messages—attacks on “enemies” and triumphant praise of their own movement. Algorithms, in turn, tend to boost posts that provoke strong reactions. Posts that evoke moral outrage or fear often achieve higher engagement and spread quickly within and across networks (Brady et al., 2017). False or misleading information may also travel farther and faster when presented in dramatic, emotional terms, as shown by studies on the viral spread of conspiracy theories and “fake news” that tap into users’ anxieties. The result is a digital public sphere filled with provocative soundbites that reinforce tribal loyalties and drown out nuance.
Empirical research highlights how these dynamics promote polarization. Recent studies show that platforms like TikTok use algorithms that reinforce emotionally charged and extremist content, leading users—especially youth—into echo chambers that normalize hate and misinformation (FAZ Dossier, 2025: 16–18). This supports the notion that discursive violence is not only rhetorical but structurally embedded in digital systems. The FAZ Dossier highlights how social media platforms are increasingly abandoning traditional moderation in favor of user-driven models, such as ‘Community Notes,’ which may fail to prevent the viral spread of misinformation (FAZ Dossier, 2025: 21–22). This shift underscores the urgency of promoting ethical communication frameworks like NVC.
A panel study on political social media use found that active engagement—such as regularly sharing, commenting, or posting political content—is linked to increased affective polarization, meaning a stronger dislike of opposing groups. In contrast, passive news consumption or simply scrolling showed no such effect (Matthes et al., 2023). This indicates that the communication style prevalent on social media, not just the content, deepens divisions. Populist communicators, with their emotionally charged and confrontational style, effectively draw followers into a constant online “us vs. them” battle that boosts in-group loyalty while fostering hostility toward outsiders. Over time, these communication patterns can normalize incivility and diminish empathy, as opponents become caricatures or enemies, and “winning” an argument takes precedence over seeking a shared truth. In this environment, the concept of free expression becomes compromised. Although it may seem that everyone can speak on social media, many voices are silenced or self-censored in the toxic atmosphere. Harassment and aggressive attacks—often launched by populist supporters against critics or minority groups—create a chilling effect on free speech, causing targeted individuals to withdraw out of fear of abuse (Amnesty International, 2020). Truly free expression involves an environment where people can share opinions and fact-based rebuttals without being drowned out by intimidation or deception.
Combating populism’s manipulative communication requires not only fact-checking or content moderation but also a cultural shift in how we communicate—moving from hostility and propaganda toward empathy and honesty. Groeben & Christmann (2023) emphasize that fair argumentation—defined by integrity, rationality, and cooperativity—can serve as a bulwark against social discord and democratic erosion. This aligns closely with Rosenberg’s Nonviolent Communication (NVC), which seeks to replace adversarial rhetoric with empathetic dialogue. This is where Rosenberg’s Nonviolent Communication framework offers a promising solution.
Rosenberg’s Nonviolent Communication (NVC): Principles and Aims
Marshall B. Rosenberg (2003)’s Nonviolent Communication (NVC) is a communication methodology rooted in compassion, empathy, and authenticity. Initially developed in the 1960s and 1970s, and elaborated in Rosenberg’s seminal work, Nonviolent Communication: A Language of Life (2003), NVC emerged from a confluence of humanistic psychology (influenced by Carl Rogers’ client-centered therapy), Gandhian nonviolence principles, and practical conflict resolution techniques. At its core, NVC seeks to transform how we relate to one another by replacing habitual patterns of blaming, coercing, or criticizing with a language of feelings and needs. Rosenberg observed that adversarial or judgmental language often provokes defensiveness and disconnection, whereas empathic communication fosters trust and cooperation. NVC aims to enable honest self-expression and respectful listening so that all parties’ underlying human needs can be acknowledged and met through creative, collaborative solutions. NVC is often taught through a structured four-component model that guides individuals to communicate with clarity and empathy (Rosenberg, 2003):
Observation (without evaluation): Describe the concrete facts or actions you observe, without adding any judgment or generalization. For example, instead of saying “You are spreading lies,” one might say “I read the post where you stated X about immigrants.” The goal is to establish a neutral starting point based on observable reality. By separating observation from evaluation, we avoid language that could trigger defensiveness and set a calmer stage for discussion. (As one NVC practitioner notes, rather than “You’re misinformed,” say “I read an article that claims XYZ,” which opens curiosity instead of conflict.)
Feelings: State one’s own emotional response to the observation or attempt to recognize the other person’s feelings. This step involves a vocabulary of emotions (e.g., “I feel frustrated and concerned when I see that claim.”). Importantly, NVC encourages taking ownership of one’s feelings rather than blaming others for them. It also invites empathic guessing of the other’s feelings, demonstrating that one is trying to understand their emotional experience. For instance, “It sounds like you’re feeling afraid and angry about the economic situation.” Naming feelings – both one’s own and the other’s – helps humanize the interaction; instead of two opposing positions, there are two human beings with emotional lives.
Needs: Behind every feeling, according to NVC, lies a human need that is met or unmet. This step articulates the deeper needs or values connected to the feelings. Rosenberg’s approach assumes a universal set of human needs (such as safety, respect, autonomy, belonging, justice, etc.) that motivate our actions. For example: “I need our community to be safe and economically secure, and I guess you also need security and recognition for your work.” In conflict, parties’ strategies may clash, but at the level of fundamental needs, there is potential for common ground. By voicing the needs, we shift attention from personal attacks to the underlying concerns that matter to everyone. Crucially, guessing the other person’s needs (with humility, not presumption) can defuse tension: “Maybe the person sharing a conspiracy theory has an unmet need for understanding or control amid uncertainty.” This does not justify false or harmful statements, but it frames them as tragically misguided attempts to meet legitimate human needs. Such reframing opens the door to compassion: we can condemn the harmful strategy while still acknowledging the human need that drives it.
Request: Finally, NVC suggests making a concrete, positive request that aims to address the needs identified, inviting collaboration. A request is not a demand; the other person should have the freedom to say no or propose an alternative. For example: “Would you be willing to look at this data together and see if it addresses your concerns about jobs being lost?” or “Can we both agree to verify claims from now on before sharing them?” The idea is to foster mutual problem-solving. In a successful NVC exchange, the request emerges naturally after empathy has been established: once both sides feel heard at the level of needs, they are more open to finding a solution that works for all. Requests in NVC are straightforward, doable, and tied to the speaker’s needs – e.g., “I’d like us to have a respectful conversation without name-calling,” rather than a vague “Stop being wrong.” This collaborative tone contrasts with the coercive or zero-sum approach often seen in polarized debates (Kohn, 1990).
Underpinning these four components is an intention of empathy and mutual respect. NVC is often described as a mindset or heart-set as much as a communication technique. It requires genuinely caring about understanding the other’s perspective and honestly expressing one’s own truth. Rosenberg emphasized that NVC is not about being “nice” or avoiding conflict, but about engaging authentically without aggression or contempt. One can still disagree strongly and even confront injustice using NVC, but the confrontation targets the issue or behavior in factual terms, rather than attacking the person’s character. For example, an NVC-informed response to hate speech might be: “When I hear you say, ‘X group is ruining our country,’ I feel alarmed and sad, because I deeply value equality and safety for all people. Would you be willing to tell me what concerns lead you to feel this way? I’d like to understand and then share my perspective too.” This response does not condone the hateful statement; rather, it calls it out as concerning yet invites the person to reveal the fears or needs behind their claim. It keeps the door open for dialogue and potential transformation.
In summary, NVC provides a framework for non-manipulative, compassionately honest communication. Instead of dueling monologues aimed at scoring points (or riling up emotions), NVC calls for dialogue aimed at mutual understanding. This orientation directly challenges the populist communication style: where populism leverages blame and anger, NVC emphasizes empathy and curiosity; where populism simplifies and demonizes, NVC humanizes and searches for underlying concerns; where populism’s goal is to mobilize a base against an enemy, NVC’s goal is to connect people to each other’s humanity and find solutions that address everyone’s needs. But can such an approach gain traction in the rough-and-tumble world of social media and political tribalism? To explore that, we now consider how NVC’s principles intersect with findings from psychology—and whether they might help counter the psychological underpinnings of populist appeal.
Emotional and Moral Underpinnings: A Psychological Perspective
The contrast between populist rhetoric and NVC can be further understood through psychological theories of emotion, morality, and intergroup conflict. Moral Foundations Theory, for instance, sheds light on why populist messaging is so potent at a gut level. Jonathan Haidt and colleagues’ theory proposes that human moral reasoning is built on intuitive foundations such as care/harm, fairness/cheating, loyalty/betrayal, authority/subversion, and sanctity/degradation (with liberty/oppression sometimes added) (Haidt, 2012). Different political or cultural groups emphasize different foundations. Populist movements (especially right-wing variants) often appeal heavily to foundations of loyalty (e.g., patriotism, defending the in-group), authority (respect for a strong leader who will restore order), and sanctity (protecting the nation’s purity or traditional values), alongside a narrative of betrayal by elites (violating fairness or loyalty) and oppression of the common people by those in power. These moral appeals trigger deep emotional responses: outrage at the corrupt elite (those who violate fairness), fear and disgust toward perceived outsiders (those who violate sanctity or security), and righteous anger that the “true people” are not being respected (violations of loyalty or authority structures). In short, populist communication succeeds by activating moral intuitions that resonate strongly with its audience’s identity and worldview. Once activated, these moral-emotional responses can bypass deliberative reasoning—the audience’s intuitive “elephant” charges ahead before the rational “rider” catches up (Haidt, 2012).
How does NVC engage with this moral-emotional landscape? Notably, NVC deliberately avoids language of good vs. evil or us vs. them that maps onto those divisive moral foundations. Instead, it appeals to universal human needs, which might be thought of as underlying the moral foundations but not tied to any one ideology. For example, rather than arguing on the level of “your loyalty to group X is misplaced,” an NVC approach would dig into why loyalty to X matters – perhaps the need for belonging, identity, or security. Those needs are human universals, even if their expressions differ. In practice, this means an NVC-inspired dialogue might sidestep the usual triggers of partisan defensiveness. A populist supporter fulminating about “protecting our country’s purity from outsiders” is clearly operating within a sanctity/loyalty moral frame. Confronting them head-on (“That’s racist and wrong!”) will likely provoke an ego-defensive reaction or even deeper entrenchment – their moral foundations feel attacked. By contrast, an NVC-informed response might be: “It sounds like you’re really worried about our community’s safety and continuity. I also care about safety – that’s a basic need we all share. Can we talk about what specifically feels threatening to you, and how we might address that concern without harming innocent people?” This kind of response implicitly acknowledges the moral concern (safety, stability) but reframes it as a shared need rather than an us–them battle. It also avoids validating any factual falsehoods or bigotry – there is no agreement that “outsiders are ruining us,” only an attempt to hear the fear beneath that statement. In doing so, NVC may help to disarm the moral intensity that populist rhetoric exploits, channeling it into a conversation about needs and solutions that includes all stakeholders’ humanity.
Another relevant psychological concept is affective polarization, which is the mutual dislike and distrust between opposing political camps. Populist communication, with its demonization of “others,” greatly exacerbates affective polarization – followers are encouraged not only to disagree with opponents, but to actively hate and fear them. As discussed, social media echo chambers further reinforce this by rewarding strident partisan content. Affective polarization is partly fueled by what psychologists call ego-involvement or identity threat. When political viewpoints become deeply tied to one’s identity and sense of self-worth, any challenge to those viewpoints feels like a personal attack or an existential threat to one’s ego. Populist narratives often heighten this effect by framing politics as an existential battle to save one’s way of life or group. In such a charged context, facts and logic alone rarely persuade – people will reject information that contradicts their group narrative because accepting it would threaten their identity (a phenomenon related to confirmation bias and motivated reasoning). Here, NVC’s emphasis on empathy and non-judgmental dialogue can mitigate ego threat.
By explicitly removing blame and personal attacks from the equation, NVC creates a safer psychological space for discussion. As one expert notes, “People don’t change their beliefs when judged and told they’re stupid or misinformed. That just shuts them down… Focusing on feelings and needs – showing human care – helps the other person be more open to a different perspective” (Seid, 2023). In essence, NVC tries to lower the defenses that come from feeling one’s identity is under siege. By first demonstrating understanding (“I hear that you’re really worried, and you value honesty in politics,”) we signal that we are not out to humiliate or annihilate the other person’s identity, which often de-escalates the confrontation. This approach aligns with conflict psychology findings that acknowledging the other side’s emotions can reduce perceived threat and open the door to persuasion. There is even emerging evidence that encouraging empathy across party lines can reduce affective polarization. One study found that when people were led to believe empathy is a strength rather than a weakness, they showed a greater willingness to engage constructively and less partisan animosity. NVC cultivates exactly this stance, treating empathy as a powerful tool rather than a concession.
A related factor is the role of ego and face-saving in public exchanges. On social media, debates often devolve into performative contests where each side seeks to “win” and save face in front of their audience. Admitting error or changing one’s view under those conditions is rare because it can feel humiliating. NVC’s philosophy addresses this by focusing on observations and personal feelings/needs instead of accusations. This minimizes the threat to the other person’s ego. For example, saying “I felt hurt when I read your comment” is less face-threatening than “Your comment was ignorant.” The former invites the person to consider your perspective without directly attacking their integrity. Over time, such small differences in phrasing and approach can create a climate where dialogue is possible without each participant staking their ego on rigid positions.
Lastly, consider the element of emotional regulation. From a psychoanalytic perspective, destructive populism operates through a perversion of the psychological function of containing: instead of processing and detoxifying destructive emotions, it amplifies and idealizes them. Democratic structures lose their capacity to absorb and transform aggression, resulting in escalating cycles of emotional escalation. Populist dynamics trigger a regression to a so-called “paranoid-schizoid mental state,” characterized by splitting, projection, and idealization. This undermines the integrative capacity of a democratic society and fosters black-and-white thinking and scapegoating. A symbiotic-destructive fit emerges between populist leaders and their followers, based on destructive narcissism. This relationship is sustained through continuous emotional escalation and mutual reinforcement of omnipotent fantasies. (Zienert-Eilts, 2020)
Populist content deliberately raises the emotional temperature – outrage, fear, and indignation are stoked because they drive engagement. NVC, by contrast, implicitly encourages slowing down and recognizing emotions rather than being driven by them impulsively. In practicing NVC, one learns to self-connect (“What am I feeling? What need is causing that feeling?”), which can prevent reactive outbursts. This self-empathy is crucial online: taking a moment to name “I’m furious at this tweet because I need honesty in our leaders” can prevent firing back an insult. It’s a form of emotional intelligence that could dampen the cycle of provocation and counter-provocation that populists rely on to keep issues inflamed. Indeed, the NVC approach to handling misinformation or extremist remarks often starts with self-empathy and calming oneself before engaging. Only then can one approach the other with genuine curiosity, rather than reactive rage. This emotional self-regulation aspect aligns with broader psychological research suggesting that interventions which reduce emotional arousal (like mindfulness or perspective-taking exercises) can facilitate more rational discussion even on contentious topics. By integrating these psychological insights, we see that NVC is not a naïve “just be nice” formula, but rather a strategy that operates on well-founded principles of human emotion and cognition: it seeks to redirect moral passion toward understanding, reduce ego defensiveness, and replace high-arousal anger with mindful dialogue.
NVC as an Antidote to Manipulative Populist Discourse
Having outlined both the nature of populist communication and the fundamentals of Nonviolent Communication, we can now draw the connections more explicitly: How could NVC serve as an antidote or counterstrategy to manipulative populist discourse, especially on social media?
First, consider the content level of communication. Populist manipulative discourse thrives on misinformation and oversimplification—sweeping claims that blame social ills on targeted groups or opponents (e.g., “The immigrants are stealing your jobs” or “The media always lies to you,”). An NVC-informed approach to countering such messages would not simply retort with facts (though fact-checking is important); instead, it would reframe the conversation around the underlying issues and needs. For example, instead of trading barbs about whether immigrants are “good” or “bad,” an NVC counter-discourse would probe: “What is the fear or hardship driving this anger toward immigrants? Is it economic insecurity? Lack of trust in the system? Let’s address that.” By doing so, it deactivates the scapegoating narrative. The focus shifts to the real causes of suffering (such as job loss due to automation or inequality) and the real needs (stable employment, community safety) that demagogic slogans have oversimplified or obscured. NVC’s emphasis on observations and needs can cut through propaganda by continually steering the discussion back to concrete reality and human concerns. It’s harder for manipulative rhetoric to take root when the audience is trained to ask, “What is the speaker feeling and needing? What am I feeling and needing?” This critical yet compassionate stance inoculates people against being swept away by slogans, as they learn to listen beneath the surface message. In fact, educational programs in media literacy and conflict resolution sometimes incorporate NVC principles to help students detect when language is manipulative or inflammatory, and to respond by seeking clarification and shared concerns rather than reacting in kind. By promoting habits of pausing and reflecting on needs, NVC serves as a kind of cognitive vaccine against disinformation and emotional manipulation.
Second, at the relational level, NVC aims to humanize the “other” and break down the us-versus-them mindset that populists promote. Populist leaders often explicitly dehumanize their opponents or scapegoats, calling them animals, traitors, or criminals—language that morally disengages their followers from feeling any empathy toward those targets. This dehumanization is a common precursor to verbal (or even physical) violence. NVC directly counters this by emphasizing the humanity of everyone involved. Practitioners of NVC seek to “attend to the humanity of everybody involved,” even while standing up to hate speech (Seid, 2023). In practical terms, this could mean that when faced with a hate-filled comment online, an NVC practitioner might respond with empathy (e.g., “It sounds like you’re really angry and hurting; I want to understand what’s behind that feeling”) rather than with an insult. This approach serves two purposes: it demonstrates to onlookers that the targeted person is not responding with hate (thus preserving their dignity and disproving the aggressor’s caricature), and it can sometimes surprise the aggressor into a more genuine conversation. There are anecdotal accounts of social media users successfully de-escalating trolls or bigoted commenters by responding with unexpected kindness or curiosity—tactics that align very much with NVC philosophy. Conversely, meeting fire with fire on social media (though understandable) often reinforces each side’s negative stereotypes. Therefore, NVC offers a toolkit for those who want to engage persuasively rather than resort to name-calling, helping to reduce the vicious cycle of escalating rhetoric.
Furthermore, NVC offers a mode of discourse that could help redefine what “free expression” entails on social media. The phrase “truly free expression” in this context suggests that current online discourse, though nominally free, is constrained by toxicity and manipulation. In an NVC-inspired vision, free expression would not merely mean anyone can post anything (the status quo, which often leads to harassment and misinformation). Rather, it implies a communication culture where individuals feel free to speak authentically—expressing their real feelings and needs—without fear of being attacked or cynically manipulated. Paradoxically, when populists weaponize “free speech,” the result is often less freedom for vulnerable voices (who are bullied into silence) and a polluted information environment that hampers everyone’s ability to speak truth. NVC can be seen as a remedy to this, encouraging norms of respectful listening and speaking that make it safer for all voices to be heard.
For example, an online forum moderated with NVC principles might encourage users to phrase disagreements in terms of “I” statements about their own feelings and needs, rather than accusatory “you” statements. Over time, this could foster trust even among users with divergent views, because they see that expressing an opinion won’t result in immediate personal attacks. In short, NVC aligns freedom of expression with responsibility of expression – the idea that we are free to say what we want, but we choose to do so in a way that acknowledges the humanity and dignity of others. This resonates with long-standing arguments that a healthy public sphere requires norms of civility and empathy to truly function in the common good, not just to maximize individual liberty to offend.
It is worth highlighting some concrete examples where a more nonviolent style of communication has made a difference. For instance, experimental studies in political psychology have shown that framing issues in terms of the other side’s moral values or shared human experiences can reduce polarization. One study found that when liberals and conservatives each reframed their arguments to appeal to the other side’s core values (e.g., arguing for environmental protection in terms of patriotism and purity of nature, rather than purely in terms of care/harm), persuasion increased significantly. This principle is akin to NVC’s approach of finding a need that underlies both sides’ concerns. Another example is dialogue programs that bring together people from opposite sides of contentious issues (such as abortion and gun control) in carefully facilitated conversations. Those programs, often inspired by empathic communication techniques like NVC, report that participants come away with reduced animosity and often find unexpected points of agreement or at least understanding. Similarly, on social media, initiatives like #ListenFirst or certain depolarization groups encourage users to practice reflective listening in comment threads. These micro-level efforts align with NVC’s core tenets and have shown anecdotal success in de-escalating what would otherwise be inflamed shouting matches.
From a critical discourse analysis standpoint, introducing NVC into social media discourse could also be seen as a form of discursive resistance. Instead of allowing populist demagogues to set the terms of debate (with their loaded language and fear-driven frames), citizens trained in NVC can subtly shift the discourse. For example, when a populist tweet declares “Group X is the enemy of the people!” an NVC-informed counter-message might redirect the focus: “I hear anger and a longing for fairness. How can we ensure everyone’s needs are considered without blaming one group?” This kind of response doesn’t directly confront the claim on its face (which might be futile with committed partisans), but it introduces an alternative narrative centered on inclusivity and understanding. If enough voices respond in that vein, the public narrative gains complexity – it’s no longer a one-note story of blame; it’s also a story about empathy and problem-solving. In the long run, such discourse could erode the appeal of purely manipulative messages, as people see a path to address grievances without vilifying others.
Challenges and Critiques: Can NVC Work Against Online Populism?
Scalability and Context
NVC was initially conceived for interpersonal or small-group communication – for example, mediating between individuals in conflict or fostering understanding in workshops. The online world of mass communication and rapid-fire posts is a very different context. One critique is whether the painstaking, time-consuming process of empathetic dialogue can be scaled to thousands or millions of people interacting on social platforms. Engaging even one hostile commenter with genuine NVC empathy can demand patience and emotional labor; doing this across an entire “troll army” or deeply polarized forum might seem infeasible.
Furthermore, text-based social media strips away tone and nonverbal cues, which are essential for conveying empathy. Without face-to-face interaction, attempts at NVC might be misinterpreted. In essence, can the NVC approach survive the chaotic, decontextualized, high-speed environment of Twitter or Facebook? Some suggest that for NVC to be scalable online, platforms would need to support it structurally – for instance, by providing guided prompts that encourage users to reflect (“What are you feeling? What do you need?”)before posting, or by highlighting posts that exemplify constructive communication. Such design changes are speculative and have not been widely implemented. Thus, in the current setup, NVC practitioners will likely find themselves swimming against a strong current of algorithmic and social incentives that favor short, incendiary content over thoughtful dialogue. This doesn’t invalidate NVC, but any realistic strategy must pair NVC with broader reforms (e.g., digital literacy education, platform moderation policies, community norms) to have a large-scale impact.
Asymmetry of Intentions
Another limitation arises from the imbalance between sincere dialogue seekers and manipulative actors. NVC assumes a baseline of goodwill – that if one expresses honestly and listens empathically, the other might do the same. But what if certain populist communicators (or their digital foot soldiers) have no interest in good-faith dialogue? Many populist leaders are adept propagandists who might see empathetic outreach as a weakness to exploit, rather than reciprocate. In online spaces, coordinated troll campaigns or extremist groups may deliberately feign personal grievances just to hijack the conversation. Engaging them with empathy might not always defuse their agenda; it could even provide more attention or a veneer of legitimacy to their hateful ideas if not handled carefully. Critics argue that NVC could be naïvely ineffective in such cases – akin to “bringing a knife to a gunfight,” or worse, bringing an open heart to a knife fight. It’s a genuine concern that must temper our expectations: NVC is not a magic wand that transforms every interaction, and some actors will simply not respond in kind.
Advocates of NVC counter that even if die-hard extremists or trolls do not change, empathic engagement can still have positive effects on the wider audience. A compassionate response to hate speech, for example, might not convert the hater, but it shows bystanders an alternative to hate, potentially preventing the spread of toxicity. Also, NVC does not forbid setting boundaries. Rosenberg himself clarified that NVC is not about being permissive or a “doormat.” One can combine NVC with firm resistance – for instance, empathizing with someone’s anger while refusing to allow abuse in a discussion (Seid, 2023). In extreme cases, protective actions (like moderation, muting, or even legal measures) are necessary; NVC distinguishes the protective use of force (to prevent harm) from punitive or retributive force. Thus, while NVC urges understanding the unmet needs driving even hateful behavior, it does not require tolerating harm or giving manipulators endless platforms. The key is to try nonviolence first, and resort to stricter measures if dialogue truly fails or safety is at risk.
Accusations of Moral Equivalence or Neutrality
A nuanced critique comes from activists and scholars who worry that the ethos of NVC – in avoiding judgmental labels like “right” and “wrong” – might slide into an amoral stance that equates oppressor and oppressed. For example, if an immigrant-rights advocate uses NVC to dialogue with a xenophobic populist, some might accuse them of “normalizing hate” or not firmly condemning a harmful ideology. There is a tension here between empathy and justice: how do we empathize with a person’s feelings and needs without appearing to excuse or legitimize dangerous beliefs? Rosenberg’s approach would say we never excuse harmful actions – rather, we separate the person (who has human needs) from their action or belief (which we can vehemently disagree with). As NVC educators emphasize, “this is in no way to excuse or condone behaviors that hurt others!” (Seid, 2023).
It is possible to hold someone accountable while treating them as a human being. Yet, in the public sphere, this nuance can be lost, and there is a risk that calls for empathy are misused to downplay the legitimate grievances of victims. NVC practitioners must be mindful of power dynamics: empathy should flow in all directions, but it must not become a tool to silence the less powerful by constantly demanding they empathize with their abusers. In practical terms, applying NVC in the populism context means walking a fine line – empathizing with, say, the economic anxieties that might fuel racist populism, without validating the racism. Some critics from feminist and anti-racist perspectives have pointed out that telling marginalized people to use NVC toward those who harm them can come off as tone-policing or burden-shifting (i.e., putting the onus on the targets of harassment to be “more understanding”).
This critique is important: any advocacy of NVC in the populist context should clarify that NVC is voluntary and context-dependent. It is a tool for those who choose to engage; it should not be a cudgel to force civility on the oppressed while the oppressor goes unchecked. In dealing with populism, perhaps the best use of NVC is by allies and moderators – those not directly targeted by the hate – who have the emotional capacity to bridge divides, rather than expecting immediate empathy from someone under attack. Additionally, there may be situations where a more confrontational approach is necessary to stop harm quickly, even if it’s not “polite” or nonviolent in tone. NVC does not claim to replace all forms of political action; it is one approach among many, best suited for communication and relationship-building, and less applicable to urgent law enforcement against incitement or structural changes to social media algorithms.
Effectiveness and Evidence
Finally, a pragmatic critique: Do we have evidence that NVC works in reducing populist influence or changing minds at scale? While NVC has a considerable track record in conflict resolution, mediation, and educational settings, there is limited empirical research on its direct impact in political persuasion or online discourse moderation. Applying NVC principles systematically to social media debates is a relatively new and experimental idea. Early indicators, as mentioned, come from small-scale dialogue experiments or individual anecdotes of depolarization. These are promising but not yet definitive proof for society-wide change.
Therefore, some observers might label NVC in this context as idealistic – a noble ideal but one facing steep odds against the structural forces of polarization and human cognitive biases. To address this, proponents suggest more pilot programs and interdisciplinary research: for example, combining NVC training with digital literacy education, or conducting controlled experiments to see if NVC-informed interventions in comment sections lead to improved outcomes (e.g., more civil tone, greater willingness of participants to engage with opposing views, reduced hate speech). If such research finds concrete benefits, it will bolster the case for broader adoption. Until then, NVC’s role in countering populism remains a plausible theory needing further validation. At the very least, it provides a vision of how communication could shift from destructive to constructive. Whether that vision can be realized will depend on experimentation, cultural change, and perhaps most importantly, individuals’ willingness to practice empathy in adversarial situations – a truly challenging task.
Conclusion
Populist movements have demonstrated a formidable ability to sway public discourse through manipulative communication – simplifying complex issues into moral dichotomies, amplifying fear and resentment, and leveraging social media algorithms to create echo chambers of anger. This article has analyzed how such “communication populism” operates not just as political messaging, but as a challenge to the very fabric of democratic dialogue and mutual understanding. In response, we have explored Marshall Rosenberg’s Nonviolent Communication as a potential antidote: a way to infuse public discourse with empathy, clarity, and respect for truth. NVC encourages a shift from accusation to inquiry, from diatribe to dialogue – focusing on the feelings and needs behind words, and on solutions that acknowledge everyone’s humanity.
Integrating insights from political communication research, we noted that populist discourse is often emotionally charged and negative, thriving on conflict and division (Engesser et al., 2017; Alonso-Muñoz & Casero-Ripollés, 2023). NVC, by contrast, works to defuse negative emotions through empathetic listening and to prevent reflexive defensiveness by removing blame (Rosenberg, 2003). From psychology, we saw that populist rhetoric taps into moral intuitions and identity needs (Haidt, 2012); NVC offers a way to address those same needs (like security, belonging, fairness) without the antagonism and scapegoating, thus potentially undercutting the appeal of the demagogue’s message. Empirical examples on social media illustrated the dire need for such approaches: content analyses show populists inundate platforms with fear-based messaging (Alonso-Muñoz & Casero-Ripollés, 2023), and user studies link these patterns to growing polarization and a chilling effect on open dialogue (Matthes et al., 2023; Amnesty International, 2020). In this light, an approach that can break the cycle – by engaging opponents with understanding, changing the tone of conversations, and re-humanizing those who have been othered – is a welcome prospect.
However, we have also critically examined whether and how NVC can overcome this challenge. We acknowledged that NVC is not a cure-all or a quick fix. Its application in the sprawling, impersonal battleground of the internet faces hurdles of scale, bad-faith actors, and misperception. It demands skill, practice, and changes in platform design or community norms to truly flourish. Moreover, empathy-driven communication must be carefully balanced with accountability and justice: showing compassion for individuals does not mean validating harmful ideologies or foregoing the protection of those targeted by hate. Rosenberg’s own writings remind us that NVC can be a powerful tool, but that sometimes a protective force is necessary. Thus, “nonviolent” communication in the context of populism should not be mistaken for passive acceptance; rather, it is an active and courageous choice to fight fire not with fire, but with water – cooling tempers, inviting reflection, and standing firmly on values of dignity and truth.
For academics and policymakers concerned with the rise of populism, the NVC framework offers fruitful avenues for further exploration. It bridges disciplines: from critical discourse analysis, it borrows the idea of challenging dominant narratives (here, challenging the narrative of enemy-making by substituting one of mutual understanding); from psychology, it leverages what we know about emotion and identity to craft communication that connects; from media studies, it raises questions about how platform ecosystems might be tweaked to reward empathy over outrage. Future research might test communication interventions inspired by NVC in online forums or deliberative democracy projects. Educators might incorporate NVC training to cultivate a new generation of digital citizens skilled in compassionate communication. Such steps could gradually build resilience in the public against manipulative rhetoric: an audience that no longer reacts blindly to fearmongering, but pauses to ask, “What is really being felt, and what is needed?”
In conclusion, the struggle against populist manipulation is not only a political or informational one, but fundamentally a communicative one – a struggle over how we speak and listen to each other in the public sphere. Nonviolent Communication, as Rosenberg envisioned it, is both a philosophical stance and a practical method that affirms the possibility of “speaking truth in love,” even amid discord. It invites each of us to reclaim our voice from the dynamics of anger and deceit, and to exercise a freedom of expression that is truly free – free from violence, free from coercion, and free to seek common humanity. While challenging to apply, Rosenberg’s approach is a counter-cultural antidote to populism’s poison, reminding us that empathy and honest connection are not naïve ideals but potent forces for social healing.
In a time of hardened divisions, listening without judgment and speaking without malice may be revolutionary acts. As we refine strategies to curb the excesses of populist communication, we should not overlook the transformative power of nonviolence in communication itself. This antidote works not by suppression, but by elevation: elevating the conversation to a plane where manipulation falters and understanding begins.
(*) Claudia Fritsch is a Psychologist and Psychotherapist in Stuttgart, Germany.
References
Alonso-Muñoz, L. & Casero-Ripollés, A. (2023). “The appeal to emotions in the discourse of populist political actors from Spain, Italy, France and the United Kingdom on Twitter.” Frontiers in Communication, 8, Article 1159847. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcomm.2023.1159847
Amnesty International. (2020). “Tweet… If you dare: Five facts about online abuse against women.” https://www.amnesty.org/en/documents/act10/1353/2020/en/
Brady, W. J.; Wills, J. A.; Jost, J. T.; Tucker, J. A. & Van Bavel, J. J. (2017). “Emotion shapes the diffusion of moralized content in social networks.” Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 114(28), 7313–7318. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1618923114
Carothers, T. & O’Donohue, A. (Eds.). (2019). Democracies divided: The global challenge of political polarization. Carnegie Endowment for International Peace.
Charaudeau, P. (2009). Discours populiste et communication politique: Les ressorts de la démagogie. (Excerpt cited in Alonso-Muñoz & Casero-Ripollés, 2023).
Druckman, J. N. & Levy, J. (Eds.). (2021). Affective polarization. Routledge.
Engesser, S.; Ernst, N.; Esser, F. & Büchel, F. (2017). “Populist online communication: Introduction to the special issue.” Information, Communication & Society, 20(9), 1279–1292. https://doi.org/10.1080/1369118X.2017.1328525
FAZ Dossier Redaktion. (2025). “Einfluss und Macht sozialer Netzwerke: Angriff der Algorithmen.” Frankfurter Allgemeine Zeitung. https://www.faz.net/aktuell/dossier-soziale-medien
Groeben, N. & Christmann, U. (2023). “Fair argumentation as a safeguard for peace and democracy.” In: C. Cohrs, N. Knab, & G. Sommer (Eds.), Handbook of peace psychology. Forum Friedenspsychologie. https://doi.org/10.17192/es2022.0073
Haidt, J. (2012). The righteous mind: Why good people are divided by politics and religion. Pantheon Books.
Helfritzsch, P. & Müller Hipper, J. (Eds.). (2024). Die Emotionalisierung des Politischen. transcript Verlag. https://doi.org/10.14361/9783839452783
Kohn, A. (1990). No contest: The case against competition. Houghton Mifflin.
Matthes, J., et al. (2023). “The way we use social media matters: A panel study on passive versus active political social media use and affective polarization.” International Journal of Communication, 17, 3211–3232.
National Institute for Civil Discourse. (Various years). Reports on social media and civility. University of Arizona.
Pörksen, B. (2018). Die große Gereiztheit: Wege aus der kollektiven Erregung. Carl Hanser Verlag.
Rosenberg, M. B. (2003). Nonviolent communication: A language of life. PuddleDancer Press.
Rosenberg, M. B. (2015). Nonviolent communication: Companion workbook. PuddleDancer Press.
Seid, A. R. (2023). “Using nonviolent communication (NVC) to address the roots and impacts of extremism.” PuddleDancer Press, online series.
Schenk, S. (Ed.). (2024). Populismus und Protest: Demokratische Öffentlichkeiten und Medienbildung in Zeiten von Rechtsextremismus und Digitalisierung. Verlag Barbara Budrich. https://doi.org/10.3224/84743033
Zienert-Eilts, K. J. (2020). “Destructive populism as ‘perverted containing’: A psychoanalytical look at the attraction of Donald Trump.” International Journal of Psychoanalysis, 101(5), 971–991. https://doi.org/10.1080/00207578.2020.1827955