DOWNLOAD REPORT
Please cite as:
Yilmaz, Ihsan; Mamouri, Ali; Akbarzadeh, Shahram & Omer, Muhammad. (2025). “Authoritarian Diffusion in the Cyberspace: How Egypt Learns, Emulates, and Cooperates in Digital Authoritarianism.” European Center for Populism Studies (ECPS). May 9, 2025. https://doi.org/10.55271/rp0097
Egypt has emerged as a key adopter and regional diffuser of digital authoritarian practices. Once limited by weak digital infrastructure, the Sisi regime has transformed the country into a technologically repressive state through sweeping legal reforms, censorship mechanisms, and expansive surveillance networks. Drawing heavily from the models of China and Russia—particularly in urban monitoring and information control—Egypt actively emulates their approaches. Crucially, both Chinese and Western technology firms have facilitated this transformation, revealing a broader pattern of global complicity. This report demonstrates how Egypt’s trajectory illustrates the transnational diffusion of digital authoritarianism through mechanisms of learning, emulation, and interdependence—and offers a stark warning to democracies about the rising threat of state-enabled digital repression.
By Ihsan Yilmaz, Ali Mamouri*, Shahram Akbarzadeh**, Muhammad Omer***
Executive Summary
This report examines the rise and entrenchment of digital authoritarianism in Egypt, spotlighting how the regime systematically reclaims and militarizes the digital space to suppress dissent and erode democratic freedoms. Digital authoritarianism in Egypt spans four key domains: restrictive legal frameworks, internet censorship, urban surveillance, and strategic digital information operations (SDIOs).
Drawing on a wide array of sources—including academic literature, human rights reports, institutional data, and credible news coverage—the report demonstrates how the Egyptian government has aggressively expanded its control over digital life. This control includes deep surveillance tactics, the criminalization of online expression, and state-sponsored manipulation of digital discourse, all contributing to the shrinking of civic space and the violation of fundamental rights to privacy and free speech.
The regime employs advanced tools such as Deep Packet Inspection (DPI), widespread website blocking, and targeted internet shutdowns to neutralize opposition. These repressive tactics are reinforced by an expansive legal arsenal that frames digital expression as a threat to national security—penalizing dissent, limiting VPN use, and compelling tech companies to align with government mandates.
At the urban level, AI-driven CCTV networks and Smart City initiatives—often developed in partnership with Chinese and Western firms—create a pervasive surveillance infrastructure, enabling real-time monitoring of public behaviour. Meanwhile, through coordinated SDIO campaigns, the regime floods social media and state-aligned platforms with pro-government narratives, systematically silencing alternative viewpoints. These operations blend defensive strategies (legitimizing the regime and quelling criticism) with offensive disinformation that delegitimizes opposition groups.
The diffusion of these practices is not solely domestically engineered. Egypt’s digital authoritarian model is transnational in character, built through mechanisms of learning, emulation, and technological dependence. China has emerged as a central enabler, exporting both surveillance infrastructure and governance models. Yet, Western corporations—including Sandvine, NSO Group, FinFisher, and Nokia Networks—have also contributed significantly, supplying critical technologies that bolster Egypt’s repressive digital architecture, often with little regard for ethical implications.
Egypt’s model of digital control illustrates a dangerous global trend: the normalization and globalization of digital authoritarianism, where regimes exploit emerging technologies and international complicity to entrench power, silence dissent, and undermine democratic norms.
Recommendations
To effectively counter the growing threat of digital authoritarianism in Egypt and beyond, a comprehensive, multi-pronged strategy must be adopted. The following recommendations highlight key interventions to safeguard digital freedoms, enhance democratic resilience, and hold both states and corporations accountable:
1. Strengthen International Cyber Norms and Regulatory Frameworks: Establish binding international standards and protocols to govern the use of digital technologies by states. These norms must explicitly prohibit mass surveillance, politically motivated internet shutdowns, and the deployment of spyware against civilians. Multilateral organizations—such as the United Nations, the European Union, and regional bodies—must play a central role in enforcing these norms through treaties, sanctions, and export control regimes that restrict the transfer of surveillance technologies to authoritarian regimes.
2. Defend Digital Rights and Data Privacy at the National and Global Levels: Push for robust data protection legislation that empowers individuals and protects them from arbitrary state surveillance. Promote digital literacy campaigns and citizen awareness programs to strengthen public understanding of online rights and safety. Support grassroots civil society organizations, independent media, and digital rights defenders who expose abuses and advocate for open, secure, and rights-respecting digital environments.
3. Enforce Corporate Accountability and Ethical Tech Governance: Hold technology firms—both domestic and transnational—legally and morally accountable for their role in enabling repression. Establish international watchdog bodies to investigate, name-and-shame, and penalize companies complicit in human rights violations through the export or maintenance of surveillance technologies. Implement mandatory human rights impact assessments for all technology exports to high-risk regimes and enhance supply chain transparency in the tech sector.
4. Promote Strategic International Collaboration to Safeguard Digital Democracy: Strengthen multilateral coalitions of democracies to share intelligence, technological tools, and policy approaches for combating disinformation, propaganda, and transnational repression. Support cross-border investigations into Strategic Digital Information Operations (SDIOs) and develop joint early warning systems to detect digital repression tactics. Extend technical and legal support to countries resisting authoritarian encroachment into their digital spheres.
5. Leverage Economic Incentives to Deter Authoritarian Partnerships: Use trade agreements, investment flows, and development aid as tools to condition engagement with states on the basis of their digital human rights records. Encourage private and public institutions to divest from companies involved in digital repression and prioritize investment in technologies that strengthen democratic institutions, secure communications, and civil society networks.
6. Deploy Diplomatic and Legal Instruments to Challenge Repression: Utilize bilateral and multilateral diplomacy to pressure authoritarian regimes to reform their surveillance laws and practices. Sponsor UN resolutions, global forums, and high-level summits that spotlight digital repression and mobilize international consensus. Support international legal actions against regimes and actors who violate digital human rights, using forums such as the International Court of Justice (ICJ) and regional human rights courts.
7. Build Resilience Through Innovation and Empowerment: Invest in the development of privacy-preserving technologies, secure communication platforms, and censorship circumvention tools. Support the creation of local digital infrastructures that resist surveillance, especially in vulnerable democracies. Back innovation ecosystems that empower civic tech, independent media, and digital rights advocacy to thrive even under authoritarian pressure.
Addressing digital authoritarianism requires more than reactive measures—it demands proactive, coordinated, and sustained global action. The recommendations above provide a roadmap for governments, international institutions, civil society, and the private sector to reclaim the digital domain as a space of freedom, accountability, and democratic possibility.
Introduction
In recent years, scholars have increasingly focused on the diffusion of authoritarianism (Ambrosio, 2010; Bank, 2017), a process where authoritarian institutions, practices, policies, strategies, rhetorical frames, and norms spread from one regime to another (Ambrosio & Tolstrup, 2019). This phenomenon is particularly pronounced in the Middle East and Muslim World, where many countries exhibit authoritarian governance (Durac & Cavatorta, 2022; Yenigun, 2021; Stepan et al., 2018; Ahmed et al., 2023; Akbarzadeh et al., 2024; Yilmaz et al., 2024).
The advent of the internet and social media in the developing world in the late 2000s significantly empowered civil society and individual activists in these regions, creating an equalizing power between the state and society (Breuer, 2012; Ruijgrok, 2017). The extensive use of these technologies by protesters led many to consider them as “liberation technology,” facilitating anti-government movements across non-democratic countries (Diamond & Plattner, 2012; Ziccardi, 2012).
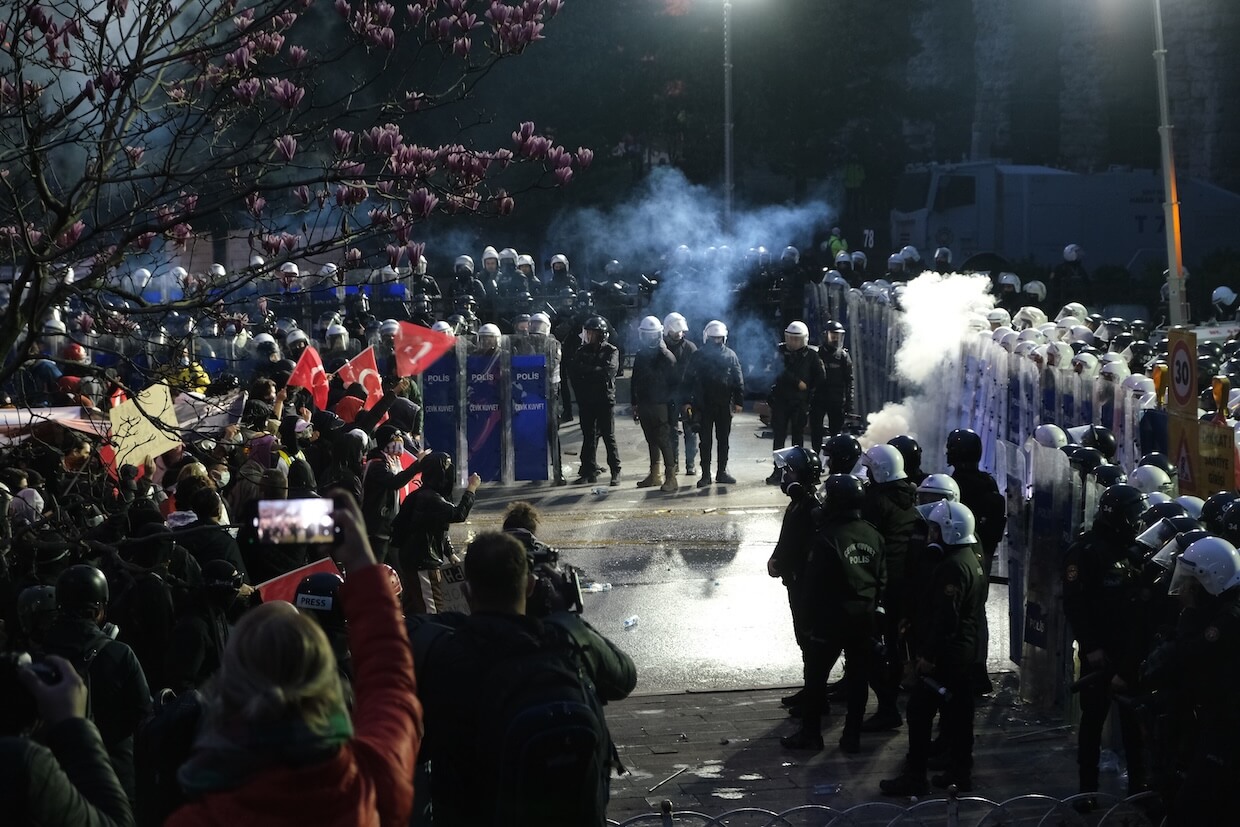
Initially, authoritarian governments struggled to control the digital sphere due to a lack of technical expertise and digital infrastructure. They often resorted to internet shutdowns, as seen in Egypt during the Arab Spring 2011 protests (Cattle, 2015). However, as digital technologies evolved, so did the capabilities of authoritarian regimes. Therefore, despite the internet’s potential as a tool for liberation, its use by authoritarian regimes to disseminate propaganda, conduct surveillance, and control information has led to a new form of authoritarianism (Polyakova, 2019).
This transformation is driven by advancements in artificial intelligence (AI), big data, and the widespread use of the internet, which have enabled unprecedented levels of surveillance and control. As Wael Ghonim, an Egyptian activist, has reminded us: “The Arab Spring revealed social media’s greatest potential, but it also exposed its greatest shortcomings. The same tool that united [people] to topple dictators eventually tore [us] apart through echo-chamber polarization, misinformation, toxic hate speech” (Gardels, 2019).
Such widespread adoption of digital control measures has led to the emergence of “digital authoritarianism” literature (Polyakova & Meserole, 2019; Dragu & Lupu, 2021; Khalil, 2020; Lilkov, 2020; Mare, 2020; Feldstein, 2019; Ahmed et al., 2023; Akbarzadeh et al., 2024; Yilmaz et al., 2024). This literature posits that as regimes leverage AI and other digital tools to monitor and control dissent, the need for policymakers and civil society organizations to counter these practices has become critical. The pessimism surrounding the potential of modern technology to undermine democracy is growing, with concerns about misinformation, data collection, surveillance, spread of conspiracy theories and propagation of authoritarian governance models (Radavoi, 2019; Stone et al., 2016; Bostrom, 2014; Helbing et al., 2019; Damnjanović, 2015; Yilmaz et al., 2025; Yilmaz & Shakil 2025). In a poll conducted by Pew, almost half of participants believed that the “use of [modern] technology will mostly weaken core aspects of democracy and democratic representation in the next decade” (Anderson, 2020).
Extant literature mainly focuses on countries such as China and Russia and their technology companies facilitating and promoting digital authoritarian practices (Khalil, 2020; Taylor, 2022; Zhang, Alon, & Lattemann, 2020). Moreover, the literature has treated policies, norms, and technological tools in a general manner as phenomena analysing authoritarian regimes’ use of tools like filtering and digital surveillance (Hellmeier, 2016; Xu, 2021) and examining policies governing the internet (Kerr, 2018). However, policies, norms, and technologies cannot be separated as they are usually interlinked among government entities, private companies, and international organizations across global networks (Dragu & Lupu, 2021). Therefore, as Adler and Pouliot (2011: 5) stated, practices are “patterned actions that are embedded in particular organized contexts,” this study chose a more holistic analysis, investigating norms, policies, and technologies employed by governments and non-state entities in an integrated manner.
This report examines the digital authoritarian practices in Egypt (see Akbarzadeh et al., 2025) and the diffusion of these practices by investigating the norms, policies, and technologies employed by the Egyptian government. What we mean by diffusion is the process that Gilardi (2012: 454) describes as what “leads to the pattern of adoption, not the fact that at the end of the period, all (or many) countries have adopted the policy.” As such, diffusion refers to the use of digital technologies by authoritarian regimes to surveil, repress, and manipulate populations (Feldstein, 2021). Therefore, diffusion does not necessarily require an absolute convergence of practices; rather, an increase in policy similarity across countries generally follows diffusion processes (Gilardi, 2010; 2012), which we demonstrate here. Egypt, similar to other authoritarian regimes, utilize digital technology—often sourced from abroad, including from Western countries—such as the internet, social media, and artificial intelligence to maintain control and suppress dissent.
We aim to understand how these practices spread and what can be done to counter them. Egypt, like other authoritarian regimes, have become adept at using sophisticated digital tools to monitor and control the internet rather than simply shutting it down. Technologies like DPI, “a type of data processing that looks in detail at the contents of the data being sent, and re-routes it accordingly” (Geere, 2012), allow for comprehensive network analysis and can be used for digital eavesdropping, internet censorship, and data theft (Bendrath & Mueller, 2011). This report will explore these dynamics in detail, providing a comprehensive analysis of the diffusion of digital authoritarianism in Egypt.
Data Analysis of the Digital Space in Egypt
Egypt, with a total population of 116 million by mid-2024 and a USD476.7 billion GDP as of 2022 (Worldometer, 2024), is considered one of the most important countries in the Middle East and has a wide influence on the Arab world. It was among the first countries to witness the Arab Spring Movement and go through dramatic changes in the political system. The internet played a significant role in this period and also in the aftermath of the military’s cope in 2013. The table below shows the rise of internet usage in Egypt.

The brief political openings in the late 2000s and the early 2010s were fuelled by the internet and social media’s empowerment of social mobilization and the authoritarian regimes’ inability to control the digital sphere as they lacked technical expertise and digital infrastructure to rein in on the internet (Cattle, 2015). However, as the use of the internet was on the rise in Egypt, the government’s efforts to control the digital space and impose more surveillance on people have been increasingly on the rise as well. Freedom House has reported a significant rise of government control on digital space in Egypt. The Freedom House Index shows that, on average, internet freedom has declined by about 40% in Egypt.
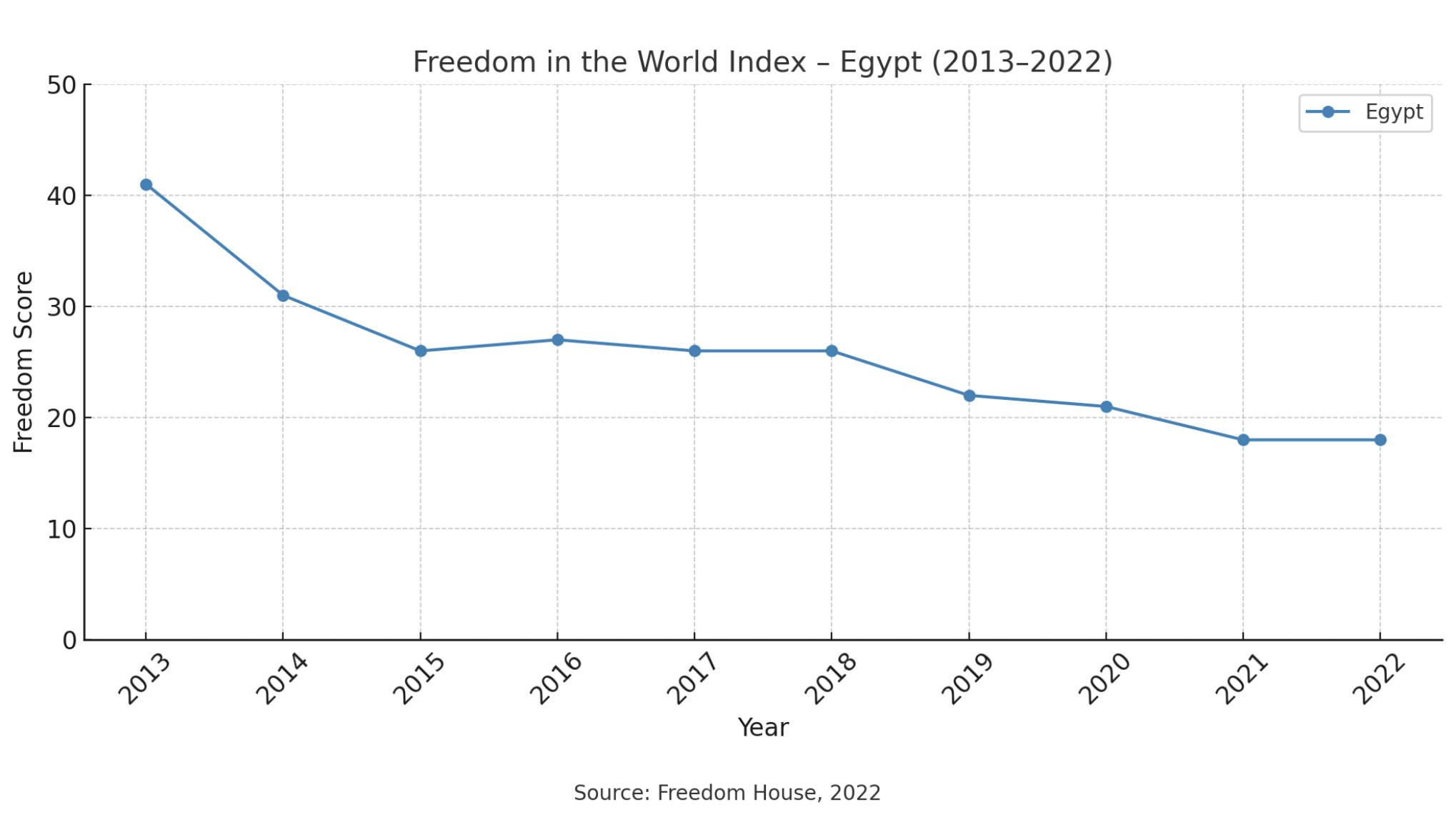
Freedom House’s World Index shows that Egypt has experienced declines in freedom of expression and belief, associational and organizational rights, the rule of law, and personal autonomy and individual rights (Freedom House, 2022). As a result, Egypt scored 26 on a scale of 0 (least free) to 100 (most free) in 2020, according to Freedom House (2021).
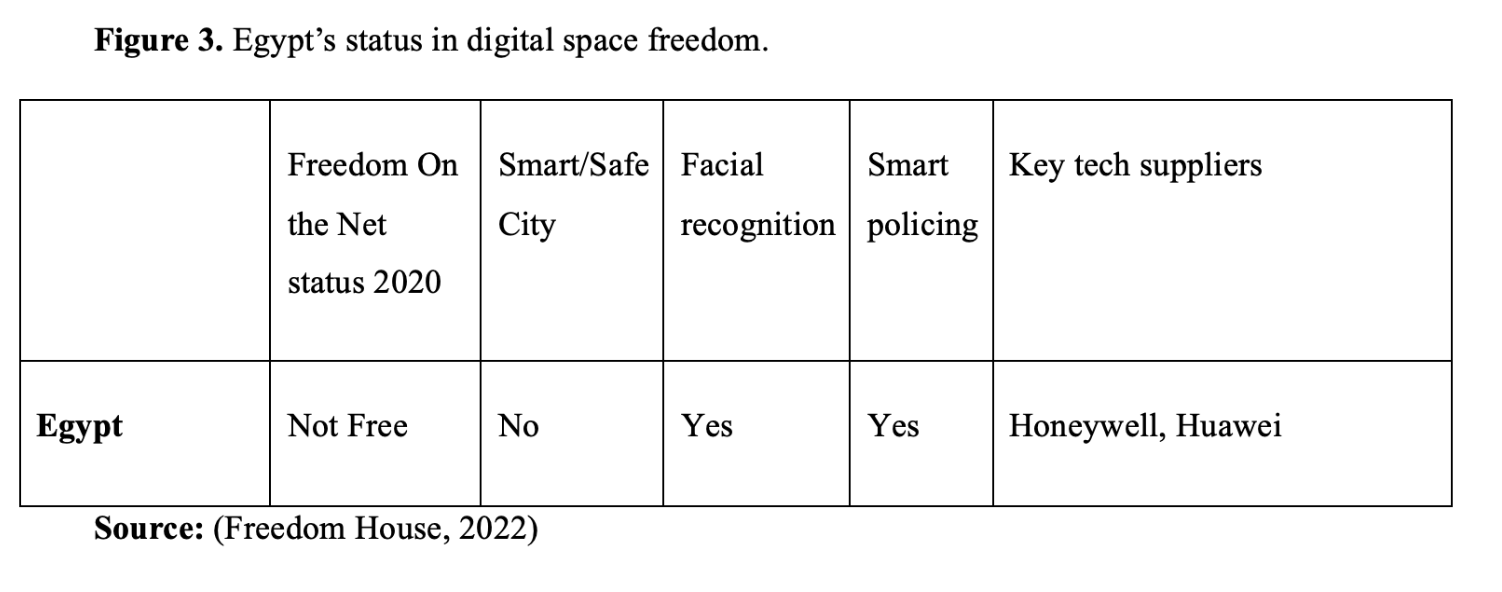
Tracing the pattern of practising digital authoritarianism in the world indicates that China and Russia play a significant role in leading this conduct, setting an effective example for authoritarian regimes in the Middle East, including Egypt, to follow the same pathway. The table in Figure 4 shows how Egypt followed the pathway of Chinese and Russian legislation in imposing digital authoritarianism.

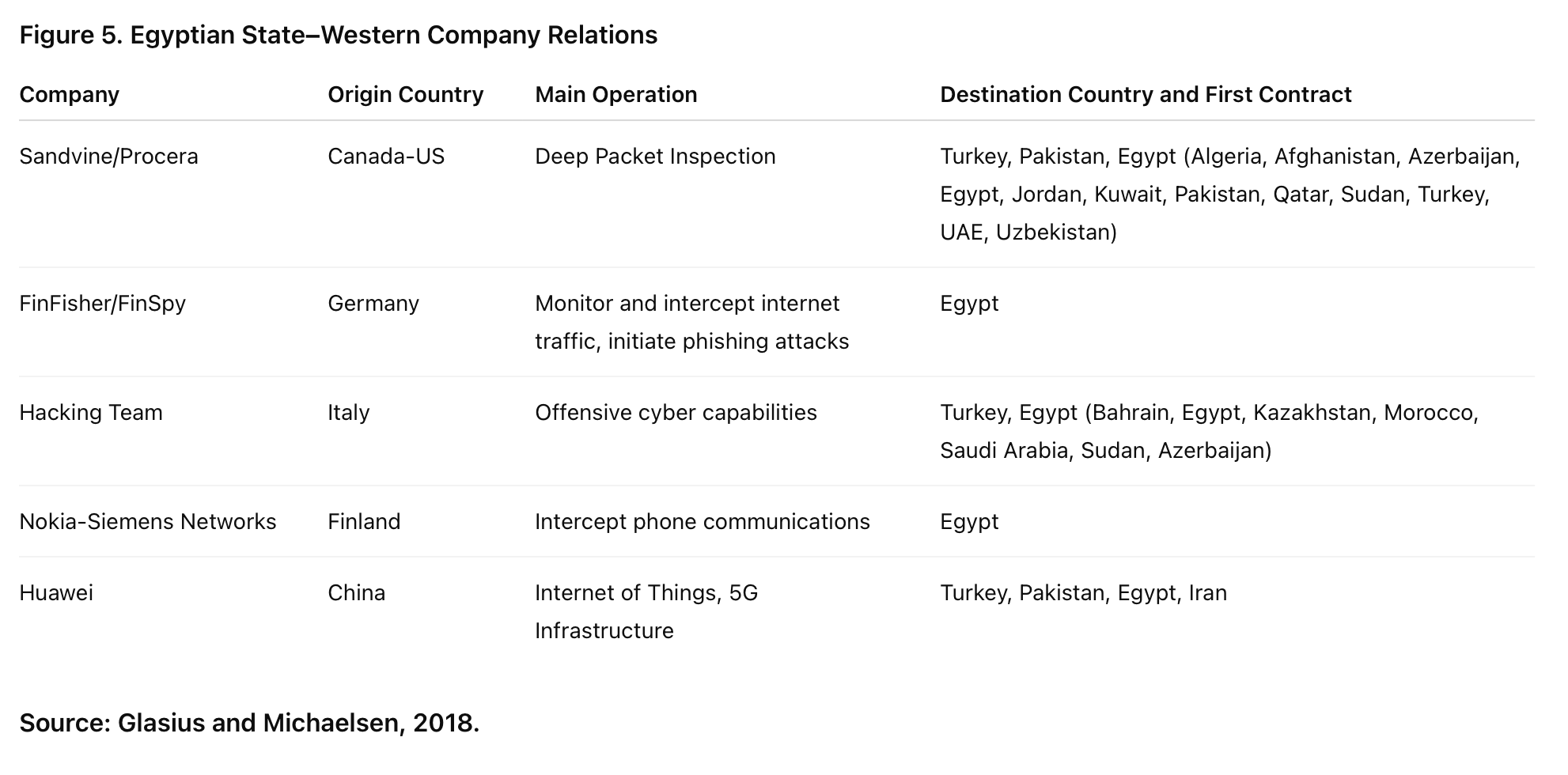
The diffusion of digital authoritarian practice in Egypt is not limited to China. Many Western companies have contributed to providing the Egyptian government with sufficient technologies to impose control on digital space. The table in Figure 5 provides details about the source of technologies used in Egypt.
Digital Authoritarian Strategies, Policies, and Practices
In this section, we explore a variety of strategies and policies the Egyptian government has adopted to impose a digital authoritarian regime in the country. The Egyptian government worked on four domains: restrictive legal frameworks, internet censorship, urban surveillance, and SDIOs. By leveraging these four domains, the Egyptian government has constructed a comprehensive system of digital authoritarianism. This system not only fortifies its grip on power but also serves as a blueprint for other authoritarian regimes seeking to exploit digital technologies to suppress dissent and maintain control.
Restrictive Legal Frameworks
Digital authoritarian regimes implement four main types of legal restrictions, and examples of all of these can be found in Egypt. First, laws that mandate internet service providers to establish systems for real-time monitoring and recording of traffic on their networks. This enables continuous surveillance of online activities. Second, legal frameworks that penalize online speech under the guise of protecting national identity, culture, and preventing defamation. This often results in the suppression of dissenting opinions and freedom of expression. Third, VPN Restrictions, which follow the lead of countries like China and Russia to ban or restrict the use of Virtual Private Networks (VPNs). While VPNs are technically legal in Egypt, many VPN servers and websites are blocked, hindering their practical use. Fourth, control over social media companies in various methods. Although Western social media sites remain accessible in Egypt, the government has introduced laws that increase its control over the content shared on these platforms. This is achieved by threatening social media companies with bandwidth restrictions and outright bans if they fail to comply with government requests. Moreover, Egypt’s 2018 Cybercrime Law requires foreign companies handling personal data within the country to designate a representative located in Egypt (Fatafta, 2020).
Despite the Egyptian Constitution guaranteeing freedom of the internet to some extent (for example, Articles 57, 68, 71, and 72), by prohibiting blocking websites, surveilling digital space, and harassing and prosecuting journalists and activists, the authorities continued to develop legislation in this direction and implement it on a large scale. Multiple legislations have been passed and applied to reach above goals.
The “cybercrime law” in Egypt, signed by President Sisi in 2018, legalizes and reinforces the existing censorship and blocking of websites (Freedom House, 2021). The new law treats all social media accounts with more than 5,000 followers as “media outlets,” making them eligible for censorship (RSF, 2018). The laws also mandated internet service providers to establish a system allowing real-time monitoring and recording of traffic on their networks (Privacy International, 2019). The cybercrime law criminalizes any form of speech that is against ‘national security’ which is defined so broadly that it covers “all that is related to the independence, stability, and security of the homeland and its unity and territorial integrity” and anything to do with the president’s office and all defence and security departments. The law permits the search of citizens’ personal devices and social media accounts can be blocked without judicial authorization, ostensibly for disseminating “false” information or inciting unlawful activities (Manshurat, 2018). Article 2 mandates that service providers retain and store records of their information systems, including all user-related data, for a period of 180 days. This information must be made available to any government agency upon request. Article 7 outlines the procedure for blocking websites that publish content deemed threatening to national security or detrimental to the country’s security or economy. Article 9 grants the Public Prosecutor the authority to issue travel bans and bring individuals accused of violating Article 7 before the Criminal Court.
The cybercrime law has led to increased penalties and harassment of journalists and activists on social media platforms (Freedom House, 2022). Consequently, there is minimal political opposition in Egypt, as expressing dissenting views on social media can lead to criminal prosecution and harsh punishments. Furthermore, there are significant restrictions and harassment of civil liberties, including freedom of expression, assembly, and the press. Security forces also engage in widespread violations against marginalized groups, including homosexuals and minorities, under the guise of national security concerns.
The Anti-Terrorism Law, passed in 2015, encompasses broad forms of criminalization and grants extensive powers to address electronic activities, including the arrest of journalists and activists, digital surveillance, and the closure and blocking of websites (Manshurat, 2020). Article 49 of this law empowers the Public Prosecution or relevant investigative authority to halt or block websites specified in Article 29 or any other aspect of online usage outlined in the legislation, as well as to confiscate devices and equipment used in the commission of such offenses. For instance, the Cairo Court of Urgent Matters issued an order to seize and freezethe assets, accounts, and properties of “Mustafa Mukhtar Mohamed Saqr,” the president of “Business News,” the company that owns the two Daily News Egypt websites.
Moreover, at the end of 2022, the Telecom Law amendments were made to expand telecommunication equipment restrictions (Rezk & Hashish, 2023). Now, not only is the importation, manufacturing, assembly of such equipment prohibited without a permit, but also possession, use, operation, installation, or marketing is prohibited without obtaining permission from relevant authorities like the NTRA (The National Telecommunications Regulatory Authority) and national security agencies. The penalty for violating these requirements has been increased to a fine ranging from 2 million to 5 million Egyptian pounds.
Internet Censorship

According to Access Now, a leading internet research organization, at least 182 internet shutdowns occurred in 34 countries in 2021 (Access Now, 2022). The Mubarak regime famously switched off the country’s internet during the mass protests in Cairo in January 2011. In recent years, however, internet shutdowns have been rare in Egypt. In 2018, the Egyptian Armed Forces ordered a region-wide shutdown of internet and telecommunication services in the Sinai Peninsula and adjacent areas during the army’s military campaign against ISIS-affiliated insurgents in the region (SMEX, 2018). One reason behind the reduction of internet shutdowns is that they are costly as they affect the delivery of essential public and private services and have been dubbed the Dictator’s Digital Dilemma (Hussain, Howard & Agarwal, 2011). Therefore, even when it is practised, the shutdown is limited to a certain location and typically lasts only a few days. According to Access Now (Hernández et al., 2023), no internet shutdown occurred in Egypt in 2021.
Common methods of censorship, which Deibert et al. (2010) highlighted as “first generation” are filtering and site blocking, which became more common in the late 2000s. IP blocking/filtering and DNS tampering are the common methods of filtering. IP filtering is used to block or filter objectionable content by restricting access to specific IP addresses. Freedom House reported in 2022 that Egypt was a not-free country in relation to the use of digital technologies, ranking it 27 out of 100, identifying three major issues: obstacles to access, limits to contents, and violation of users’ rights (Freedom House, 2022).
Since the imposition of a “state of emergency” in Egypt in 2017 (Atlantic Council, 2019), which directly granted the authorities the power to impose censorship and monitor all forms of online communication, Egypt blocked over 500 websites (AFTE Egypt, 2020). This includes independent news websites that publish articles criticising the Egyptian government, such as Mada Masr, Al-Manassa and Daily News Egypt, in addition to international news websites, such as Al-Jazeera, Al-Arabiya, and Huffington Post Arabic. The blocking also included well-known Egyptian blogs that had previously warned since Sisi took power that he was rebuilding an authoritarian regime. The banned blogs included Fahmi Huwaidi’s blog (including his column in Shorouk News), Jawdell’s blog, Manal’s blog, Alaa’s blog, Bahia’s blog, and Ahmed Gamal Ziada’s personal blog. Manal and Alaa had previously won awards (Welle, 2005) from Reporters Without Borders. The blocking expands websites that provide content related to human rights and civil society, such as the website of Reporters Without Borders, the Arabic Network for Human Rights Information (ANHRI), the Egyptian Commission for Rights and Freedoms, the Journalists Against Torture Observatory, and the website of Human Rights Watch, one day after the organisation released a report documenting the systematic use of torture in prisons in September 2017. The blocking was not limited to news sites only but also went on to block 261 VPN and proxy sites, including “Tunnelbear,” “CyberGhost,” “HotspotShield,” and messaging application Signal.
Censorship sometimes occurs via prosecution measures, which come in conjunction with punishing the authors or contributors. Egyptian authorities severely undermined media freedom and the right to access information and punished the publication of opinions on news sites and social media posts. For example, in February 2023, the Public Prosecution referred three journalists (Welle, 2023) from Mada Masr to trial in a case related to publishing a report alleging corruption in the pro-Sisi “Nation’s Future Party,” and in June, the authorities blocked two independent news websites, “Egypt 360” and “The Fourth Estate” (Access Now, 2023). In September 2023, security forces arrested two individuals from their homes in Menoufia and Mansoura governorates after they published tweets on the “X” website, supporting Tantawi and democratic change. In October 2023, the Supreme Council for Media Regulation referred workers (“x.com,” n.d.) at the independent media website “Mada Masr” to the prosecution, with the charge of “practising media activities without a license” and “spreading false news without verifying its sources.”
Authoritarian regimes have tended to use more subtle and insidious forms of censorship, which also use surveillance techniques and rely on quasi-democratic legal mechanisms (Deibert & Rohozinski, 2010). This has included using DPI surveillance technology acquired from Western and Chinese companies, which have become essential sources of diffusion of authoritarian practices. Companies such as Sandvine Corporation, a US-Canadian company, have provided tech to over a dozen countries, including Egypt. DPI is “a type of data processing that looks in detail at the contents of the data being sent and re-routes it accordingly” (Geere, 2012). DPI inspects the data being sent over a network and may take various forms of action, such as logging the content and alerting, as well as blocking or rerouting the traffic. DPI allows comprehensive network analysis. While it can be used for innocuous purposes, such as checking the content for viruses and ensuring the correct supply of content, it can also be used for digital eavesdropping, internet censorship, and even stealing sensitive information (Bendrath & Mueller, 2011).
Urban Surveillance
In addition to digital monitoring, the government has significantly expanded its surveillance capabilities within urban areas. Advanced surveillance systems, including extensive CCTV networks equipped with facial recognition technology, have been deployed. These systems are integrated with AI-powered analytics capable of tracking and identifying individuals, monitoring public gatherings, and analysing behavioural patterns. This pervasive surveillance infrastructure not only deters public dissent but also enables the rapid identification and apprehension of activists and protesters.
Egypt has employed extensive surveillance technologies such as Smart City/Safe City platforms, facial recognition systems, and smart policing, as highlighted in the AI Global Surveillance (AIGS) Index. These technologies have been instrumental in suppressing democratic movements (Wheeler, 2017). During the 2010s, Egypt witnessed increased internet technology adoption and a concurrent decline in democratic practices. Data from the International Telecommunication Union (ITU) indicates a dramatic rise in internet usage in Egypt since 2019, which led the Egyptian government to more investment in urban surveillance.
The aforementioned DPI technology acquired from the American company Sandvine/Procera Networks enabled the Egyptian government to monitor citizens’ internet activities, hack accounts, and reroute internet traffic. This technology allows Telecom Egypt to spy on users and block human rights and political content (Marczak et al., 2018). Additionally, Egypt’s General Intelligence Service has conducted sophisticated cyber-spying operations on opposition and civil society activists by installing software on their phones, granting access to files, emails, GPS coordinates, and contact lists (Bergman, 2019).
Safe or smart cities are another policy that Egypt is undertaking in order to increase its urban surveillance capabilities. The “Smart” concept generally involves gathering large amounts of data to enhance various city functions. This can include optimizing the use of utilities and other services, reducing traffic congestion and pollution, and ultimately empowering both public authorities and residents. According to a Huawei report, “Safe cities are an essential pillar supporting the future development of smart cities” (Hillman & McCalpin, 2019). These cities deploy high-speed communication networks, sensors, and mobile apps to enhance mobility, connectivity, energy efficiency, service delivery, and overall resident welfare (Hong, 2022). Becoming “smart” typically involves harnessing troves of data to optimize city functions—from more efficient use of utilities and other services to reducing traffic congestion and pollution—all with a view to empowering public authorities and residents (Muggah, 2021). With the advance of CCTV and AI technology, urban surveillance capabilities have grown exponentially over the past ten years. Dubbed “safe” or “smart” cities, these urban surveillance projects are “mainly concerned with automating the policing of society using video cameras and other digital technologies to monitor and diagnose suspicious behaviour” (Kynge et al., 2021).
Egypt’s most significant smart city project under the Sisi government is the New Administrative Capital (NAC) east of Cairo (Al-Hathloul, 2022). The NAC is designed with a full suite of smart/safe city solutions, including 6,000 CCTV cameras and a surveillance system by American company Honeywell, which monitors crowds, traffic congestion, theft, and suspicious activities and triggers automated alarms during emergencies (Mourad & Lewis, 2021). Honeywell also has contracts for Saudi Arabia’s NEOM megaproject. Huawei’s presence in Egypt has also been growing. In 2018, Huawei signed a memorandum with Telecom Egypt to establish a $5 million data centre for a cloud computing network, aiming to develop one of the five largest cloud networks globally and the first in MENA. Egypt and Huawei are also negotiating to bring Huawei’s 5G infrastructure to the country (Blaubach, 2021). The surveillance infrastructure includes Schneider Electric’s EcoStruxure platform, which connects various systems for optimization and sustainability (Egypt Today, 2022).
The development of smart city infrastructures has sparked controversies, with critics arguing that these technologies enable pervasive collection, retention, and misuse of personal data by law enforcement and private companies. The NAC, which is being built by China State Construction Engineering Corporation (CSCEC) (Al-Hathloul, 2022), has been driven by an attempt by the authoritarian Sisi government to isolate and protect itself from a revolutionary scenario that befell the Mubarak regime in 2011. By moving government offices 50 km away from central Cairo and Tahrir Square, the regime aims to ensure its structures are safeguarded even during unrest. All the surveillance capabilities in the NAC will be further helpful in protecting the regime (see Middle East Monitor, 2021; Bergman & Walsh, 2021; Menshawy, 2021).
Strategic Digital Information Operations (SDIOs)

The Egyptian government employs a sophisticated network of SDIOs. SDIOs refer to “efforts by state and non-state actors to manipulate public opinion as well as individual and collective emotions by using digital technologies to change how people relate and respond to events in the world” (Yilmaz et al., 2023). Thus, the Egyptian government does not only rely on randomized acts of internet shutdowns but carefully manipulates and alters the information environment to serve its motives.
Egypt has begun to move beyond strategies of ‘negative control’ of the internet, in which regimes attempt to block, censor, and suppress the flow of communication and toward strategies of proactive co-optation in which social media serves regime objectives. The opposite of internet freedom, therefore, is not necessarily internet censorship but a deceptive blend of control, co-option, and manipulation. Scholars call this phenomenon ‘flooding’ as the governments try to ‘flood’ the informational space with false, distracting or otherwise worthless pieces of information (Roberts, 2018; Mir et al., 2022). As the public debate is seeded with such disinformation, this makes it hard for the governments’ opponents to convince their supporters and mobilize.
The Egyptian government employs a robust propaganda machine to shape public perception and maintain control over the narrative. This involves the strategic use of state-controlled media, social media platforms, and online influencers to disseminate pro-regime content and discredit opposition. The regime propagates conspiracy theories that portray political dissenters as foreign agents or terrorists, thereby justifying its repressive measures. As Akbarzadeh et al. (2025) demonstrates, “President Abdul Fattah al-Sisi frequently talks about conspiracies against the Arab World and Egypt in particular, thanking Egyptians who stood against these conspiracies and prevented the country from falling in the direction of Iraq, Syria, and Libya, all that were intervened by the US and other Western allies.” In the same way “Sisi used the consequences of the Western role in Iraq, Syria, and Libya as a method to promote his rule in Egypt and scare Egyptians from seeking change in their country, which would lead them to get trapped in conspiracies undertaken in other Middle Eastern countries” (Akbarzadeh et al., 2025).
Egyptian officials commonly instil fear among citizens to ensure their loyalty to the current government, often by amplifying concerns about potential conspiracies against the nation. This rhetoric tends to escalate as elections approach (Akbarzadeh et al., 2025). State-run TV channels, newspapers, and online portals play a crucial role in this information warfare, ensuring that the regime’s message reaches a broad audience. The Sisi regime, for example, employs troll armies to be used in political astroturfing operations. In 2020, Twitter banned over 9,000 accounts that were spreading misleading information. Another report found that the Sisi government used automated/bot accounts to promote its popular hashtags on Twitter (DFRLab, 2023).
The regime usually employs defensive and offensive approaches in this regard. The dual strategy, seamlessly blending defensive and offensive tactics, creates a narrative that reinforces the regime’s image and marginalizes any alternatives, fostering an environment of public trust and unity under the existing leadership.
Defensively, it seeks to portray the regime as a legitimate national authority, emphasising its adherence to the nation’s interests and well-being in a way that no legitimate alternative is imaginable. In these narratives, government leaders are portrayed as heroic figures with exceptional qualities, and the system is presented as flawless and well-suited to the country’s needs. Like many examples Igor Golomstock provided in his book Totalitarian Art (1990), Egyptian propaganda presents the head of state as the father of the nation, and any attempt to criticise him or his authority is introduced as a betrayal to Egypt. Egyptian TV channels frequently host Arab leaders praising Sisi and portraying him as the savour of Egypt and the Arab nation.
On the offensive front, the propaganda machine works to discredit any alternative to the current regime. Opposition figures or movements are subjected to character assassinations and labelled as traitors, criminals, or foreign agents. Conspiracy theories are propagated, linking opposition figures to nefarious plots or foreign interference, thereby undermining the credibility of opposing narratives. Additionally, the propaganda machine manipulates national unity sentiments to marginalise dissent, presenting the regime as a unifying force and framing opposition as divisive threats to the country’s unity. This comprehensive approach aims to fortify public support for the current regime while systematically diminishing the credibility of dissenting voices. In conjunction with the magnification and glorification of the president’s image, extensive work has been done to demonise the image of the opposition as a whole, generalising all under the unsightly titles of “traitors” cooperating with foreign enemies, “terrorism,” “riot” and “suspicious calls,” slamming all attempts of demonstrations or criticising the government.
One significant rationale lies in the inherent lack of genuine legitimacy, coupled with a substantial disconnect between the state and society. Consequently, the fabrication of imaginary adversaries becomes a tool for fostering national unity and identity under the regime’s rule. A parallel goal of this strategy is the cultivation of a cult of leadership. Totalitarian regimes craft an image of leaders as defenders against external enemies, fostering a cult of personality that solidifies their control over the narrative and the populace. This narrative, in turn, rallies support for the militarization of both the state and society. Moreover, the identification of enemies becomes a rationale for increased militarization and defence spending. Totalitarian regimes leverage perceived external threats to justify allocating resources to the military, enhancing capabilities, and maintaining control over the security apparatus. Consequently, these regimes effectively maintain fear and control over the population. Ultimately, the perpetual portrayal of an external threat or identification of internal enemies sustains a climate of fear among citizens, discouraging challenges to the regime.
In authoritarian regimes, conspiracy theories play a crucial role in consolidating power by channelling public discontent toward perceived external or internal threats. These narratives function as propaganda tools, allowing governments to justify repression, delegitimize critics, and deflect attention from governance failures. Unlike in democratic contexts, where conspiracy theories are often propagated by fringe actors, authoritarian regimes institutionalize them, presenting them as official truths that shape political realities. A key tactic involves accusing dissidents of affiliations with groups like the Muslim Brotherhood to suppress freedom of speech, protest, and independent media. By framing opposition figures as existential threats to national unity, regimes cultivate public trust and reinforce their own legitimacy while silencing alternative voices (Akbarzadeh et al., 2025).
Collectively, the sophisticated implementation of SDIOs manipulate feelings of national unity to marginalise the opposition, presenting the regime as a unifying force and framing the opposition as a divisive threat to the country’s unity. This comprehensive approach aims to strengthen popular support for the current regime while systematically diminishing the credibility of opposition voices. The dual strategy, which seamlessly blends defensive and offensive tactics, creates a narrative that enhances the regime’s image and marginalises any alternatives, fostering an environment of public trust and unity under the current leadership.
Diffusion of Authoritarian Practices

Diffusion mechanisms are systematic sets of statements that provide a plausible explanation of how policy decisions in one country are influenced by prior policy choices made in other countries (Braun & Gilardi, 2006; 299). The literature on this topic often highlights areas of convergence and contact points between early and later adopters (see Kerr, 2018). Diffusion is any process where earlier adoption or practice within a population increases the likelihood of adoption among non-adopters (Strang, 1991: 325). It occurs when policy decisions in one country are systematically influenced by previous policy choices in other countries (Dobbin et al., 2007: 787; Gilardi, 2012). Traditionally, research on diffusion has focused on the spread of popular uprisings against autocratic leaders (Koesel & Bunce, 2013; Beissinger, 2007). However, more recently, scholars have shifted their focus to the diffusion of authoritarian practices (Ambrosio, 2010; Bank, 2017). The diffusion process occurs through three main mechanisms: learning, emulation, and cooperative interdependence (Bashirov et al., 2025).
Learning
The process of learning can be driven internally, where actors learn from their own experiences, evaluating and adopting innovations based on the success of prior applications. It can also be externally driven, with an external actor facilitating the learning process. The role of the external actor can range from small, such as selling or installing technological tools, to extensive, involving large-scale activities like seminars and training programs to promote a policy or practice. Using a practice framework, we focus on ‘configurations of actors’ involved in enabling authoritarianism (Michaelsen, 2018). Often, these actors are private companies rather than states.
Contrary to the perceived active role of Chinese companies, it was Western tech companies that provided most of the high-tech surveillance and censorship capabilities to authoritarian regimes in the Muslim world. Notable examples include the US-Canadian company Sandvine, the Israeli NSO Group, German FinFisher, and Finland’s Nokia Networks. Internet surveillance has been facilitated through the cooperation between adopter countries willing to purchase the technology and companies like Sandvine willing to sell it. Sandvine’s willingness is evidenced by the company’s chief technology officer, who stated, “We don’t want to play world police. We believe that each sovereign country should be allowed to set their own policy on what is allowed and what is not allowed in that country” (Gallagher, 2022).
Regarding external learning, China, along with Chinese and Western private companies, has been leading the promotion of internet censorship practices. China has become a major advocate and a learning source for middle powers in internet surveillance, data fusion, and AI. The Shanghai Cooperation Organization (SCO) has become a crucial platform for these efforts. For instance, at the 2021 SCO summit, Chinese officials led a panel called the Thousand Cities Strategic Algorithms, training an international audience, including many representatives from developing countries, on creating a “national data brain” that integrates various forms of financial and personal data and employs artificial intelligence for analysis. According to the SCO website, 50 countries are involved in discussions with the Thousand Cities Strategic Algorithms initiative (Ryan-Mosley, 2022). China has also been proactive in offering media and government training programs to representatives from countries affiliated with the Belt and Road Initiative (BRI). A notable example includes the Chinese Ministry of Public Security directing Meiya Pico, a Chinese cybersecurity company, to train government representatives from Turkey, Pakistan, Egypt, and other nations on digital forensics (see Weber, 2019: 9-11).
Russia is another leading source of diffusion of digital authoritarianism in the Middle East. Russia’s brazen attempts at disinformation and propaganda lend support to the emergence of digital manipulation as an acceptable practice across authoritarian countries. By demonstrating the effectiveness of disinformation campaigns and propaganda – such as Russian interference in US presidential elections in 2016 – the country has shown other regimes that similar tactics can be used to control their own populations and advance their interests (Day, 2022).
The role in the diffusion of digital authoritarian practice in the Middle East is not limited to China and Russia. Western countries, in fact, played significant roles as well. Despite Huawei’s involvement in projects like the $5 million data centre with Telecom Egypt and discussions about 5G infrastructure, Egypt has shown a preference for Western technology in its major smart city projects, like the New Administrative Capital (NAC). The adoption of urban surveillance capabilities in Egypt is thus a result of both internal and external learning mechanisms. The Sisi regime’s strategies, especially in the NAC, reflect an attempt to insulate the government from potential unrest.
US-Canadian company Sandvine/Procera has provided DPI surveillance equipment (hardware and software) to national networks operating in Egypt (Telecom Egypt). This system operates over connections between an internet site and the target user and allows the government to tamper with the data sent through an unencrypted network (HTTP vs. HTTPS). Moreover, recent revelations show that the company has played a significant role in facilitating the spread of ideas between countries. In an internal newsletter sent to employees, Sandvine Chief Technical Officer Alexander Haväng wrote Sandvine’s equipment could “show who’s talking to who, for how long, and we can try to discover online anonymous identities who’ve uploaded incriminating content online.” Through their information campaign, Sandvine contributed to learning by governments. In Egypt, the government has been using Sandvine’s devices “to block dozens of human rights, political, and news websites, including Human Rights Watch, Reporters Without Borders, Al Jazeera, Mada Masr, and HuffPost Arabic” (Marczak et al., 2018: 8).
Emulation
Emulation can be defined as “the process whereby policies diffuse because of their normative and socially constructed properties instead of their objective characteristics” (Gilardi 2012: 467). Research has shown that in complex and uncertain environments, policymakers respond by emulating the structural models of recognized leaders in the domain (Barnett & Finnemore, 2005). This behaviour is primarily driven by the pursuit of legitimacy and harmonization. International organizations, both governmental and non-governmental, play a crucial role in spreading commonly accepted standards of behaviour and organizational structures among countries.
Emulation has been significant in the diffusion of legal norms regarding internet restrictions and, to a lesser extent, in adopting Chinese urban surveillance infrastructures. Chinese corporations have established training hubs and research initiatives to disseminate expertise in artificial intelligence, internet surveillance, and digital space management (Kurlantzick, 2022). For instance, Huawei set up an OpenLab in Egypt in 2017, focusing on smart city, public safety, and smart government solutions. China has been a major promoter of the ‘safe city’ concept, which focuses on surveillance-driven policing of urban environments. This approach has been refined in many Chinese cities (Triolo, 2020). Companies such as Huawei, ZTE Corporation, Hangzhou Hikvision Digital Technology, Zhejiang Dahua Technology, Alibaba, and Tiandy are leading the export of this model (Yan, 2019).
Moreover, homophily, in the form of cultural and political alignment, as well as China’s emergence as an authoritarian role model, contributed to the emulation process. Homophily among actors played an important role, as actors prefer to emulate models from reference groups with whom they share similar cultural or social attributes (Elkins & Simmons, 2005). Political alignment and proximity among nations foster communication and the exchange of information (Rogers, 2010). This dynamic is observed between China and Russia and political regimes in the Muslim world including Egypt, which are susceptible to varying degrees of authoritarian governance. Loan conditionalities and trade negotiations within the context of China’s Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) have also played a role in enabling the spread of censorship and surveillance technologies from China to the Muslim world.
The Egyptian government has gathered widespread spying and phishing capabilities sourced from mostly Western companies. An obscure wing of the General Intelligence Directorate called the Technical Research Department (TRD) has purchased equipment from Finland-based Nokia-Siemens Networks (now Nokia Networks) that permits dial-up internet connection, enabling users to access the internet even if the primary national infrastructure is offline. Furthermore, Nokia Siemens Networks has provided the Egyptian government with an interception management system and a surveillance hub for fixed and mobile networks, granting the government mass surveillance capabilities to intercept phone communications (Privacy International, 2019). Another company involved in Egypt was the Italian surveillance technology company Hacking Team. In 2015, the latter was contracted by both the TRD (Technical Research Department) affiliated with Egyptian intelligence, and the Mansour Group (a conglomerate belonging to the second richest family in Egypt) to provide malware that grants the attacker complete control of the target computer (Privacy International, 2019).
In a brazen example of emulation of the practices of other authoritarian states, the Egyptian government started a widespread phishing campaign called Nile Phish in 2016 against the country’s civil society organizations implicated in the Case 173 crackdown (Scott-Railton et al., 2017). The campaign involved sending predatory emails and text messages to members of civil society to hack into their devices and accounts. An Amnesty International Report (2020) revealed that the Egyptian government used spying technology called FinSpy supplied by German company FinFisher Gmbh. FinSpy is a computer spyware suite sold exclusively to governments to monitor and intercept internet traffic, as well as to initiate phishing attacks against targeted users. FinSpy Trojan has been in use in Egypt to spy on opposition movements and enable the surveillance of political activists and journalists (ECCHR, 2023). In addition, denial-of-service (DoS) or packet injection practices are common in Egypt. For example, between May and September 2023, former Egyptian MP Ahmed Eltantawy was targeted by Cytrox’s Predator Spyware via links sent on SMS and WhatsApp. Eltantawy had announced he would be running in the 2024 presidential elections. Citizen Lab found that the network injection attack could be attributed to the Egyptian government and Sandvine’s PacketLogic product (Marczak et al., 2018).
Cooperative Interdependence
The practice of cooperative interdependence in the context of digital technologies refers to how internet censorship and surveillance are enabled through collaboration among adopting countries and state actors and private companies like Sandvine and NSO Group. Both Sandvine and NSO Group have faced significant controversy in their home countries, the US and Israel, over selling surveillance products to authoritarian regimes in the Middle East and beyond, Egypt in particular as explained in this report. NSO Group has been banned by the Israeli government from selling its products to major clients in the Middle East, including Saudi Arabia and the UAE (Staff, 2021). Similarly, Sandvine ceased operations in Russia following US sanctions after Russia’s invasion of Ukraine in 2022 and was forced to stop selling equipment to Belarus after reports revealed its technology was used by the Lukashenko regime to suppress protests in 2021 (Gallagher, 2022).
The broad process of digital authoritarian diffusion has created cooperative interdependence between the involved parties. Through cooperation with global actors, both corporate and state-level, Egyptian governments have imported sophisticated technologies enabling comprehensive internet and urban surveillance. Cooperative interdependence occurs when the policy choices of some governments create externalities that others must consider, leading to mutual benefits from adopting compatible policies (Braun & Gilardi, 2006). This dynamic incentivizes decision-makers to adopt policies chosen by others, enhancing efficiency and yielding mutual benefits. Here, China leverages its Digital Silk Road (DSR) under the BRI to promote the adoption of its technological infrastructure and accompanying surveillance and censorship policies (Hillman, 2021).
For instance, at the 2017 World Internet Conference in China, representatives from Egypt, Turkey, Saudi Arabia, and the UAE signed a “Proposal for International Cooperation on the ‘One Belt, One Road’ Digital Economy” to construct the DSR, enhancing digital connectivity and e-commerce cooperation (Laskai, 2019). Core components of the DSR include smart cities, internet infrastructure, and mobile networks. Rather than forcing these countries to adopt internet censorship practices, China alters the incentive structures of BRI-connected states. Financial incentives, coupled with technology transfer, promote China’s practical approach to managing cyberspace. The DSR’s digital projects—such as 5G networks, smart cities, fibre optic cables, data centres, satellites, and connecting devices—have commercial value and strategic benefits, helping China achieve its geoeconomic and geopolitical objectives by promoting digital authoritarian practices and its internet governance model (Malena, 2021; Tang, 2020).
Conclusion

This research has demonstrated the mechanisms through which digital authoritarian practices diffuse in Egypt. We found that Egypt has enacted multiple policies, including restrictive legal frameworks, internet censorship, urban surveillance, and strategic digital information operations (SDIOs), to reclaim the digital space from opposition and civil society, thereby entrenching digital authoritarianism in the country. The models adopted by the Egyptian regime closely emulate China and Russia’s paradigms of internet sovereignty and information control. China’s extensive political and economic linkages with Egypt, its strategic role in regional economies, and its leadership in forums like the Shanghai Cooperation Organization (SCO) have facilitated this trend. Through initiatives such as the Belt and Road Initiative (BRI), China has exported its digital governance model while positioning itself as a global leader in information technology (Ryan-Mosley, 2022; Weber, 2019).
The diffusion of surveillance and censorship technologies also reflects a complex learning process involving both state and corporate actors. While China has played a critical role in promoting internet censorship practices, private Western companies have equally enabled Egypt’s digital authoritarian turn. Companies such as Sandvine, NSO Group, FinFisher, and Nokia Networks have supplied surveillance infrastructure independently of state policy, a departure from conventional diffusion literature that associates such practices with national strategic interests (Gallagher, 2022; Marczak et al., 2018; Privacy International, 2019). For instance, Sandvine’s DPI technology has been used in Egypt to block dozens of news and human rights websites, while its executives openly dismiss responsibility by deferring to national sovereignty (Gallagher, 2022). This corporate-led diffusion challenges the notion that digital authoritarianism is solely state-driven and reveals an under-regulated global market in repressive technologies.
Our findings have three broader implications. First, while Chinese influence is significant, the role of Western technology firms in enabling authoritarian diffusion should not be underestimated. Their operations in Egypt have not been directly aligned with their home states’ policies, contradicting earlier findings that firms facilitating authoritarian practices often act under state guidance (Arslan, 2022). Second, these private firms are not only exporters of tools but are actively involved in implementing government-sanctioned strategies, including malware distribution and interception systems (Appuhami et al., 2011; Teets & Hurst, 2014). Third, the study identifies the mechanisms of diffusion—learning, emulation, and cooperative interdependence—as key to understanding how regimes adapt digital authoritarian tactics to shifting political and technological contexts (Braun & Gilardi, 2006; Dobbin et al., 2007; Gilardi, 2012; Strang, 1991; Kerr, 2018).
Developing states may increasingly adopt practices such as national firewalls, smart city surveillance, and social credit systems modelled on early adopters like China and Russia. As they become embedded in transnational authoritarian networks—whether through SCO summits or Digital Silk Road initiatives—these regimes are incentivized to replicate practices that strengthen regime durability and evade democratic scrutiny (Hillman, 2021; Malena, 2021; Tang, 2020; Laskai, 2019).
Given these trends, addressing the entrenchment and diffusion of digital authoritarianism requires a coordinated, multi-level response. There is an urgent need to institutionalize international cyber norms and regulations that clearly define and prohibit practices such as mass surveillance, politically motivated internet shutdowns, and spyware exports. Multilateral institutions, including the United Nations and the European Union, must lead the effort to develop enforceable standards, promote transparency, and strengthen export control regimes. This would include holding corporations accountable through mandatory human rights due diligence, transparency disclosures, and legal sanctions when they contribute to repression.
Defending digital rights also requires robust national privacy protections and support for civil society organizations operating under authoritarian conditions. These groups need financial resources, digital tools, and international solidarity to resist surveillance, educate the public, and pursue legal redress where possible. Supporting democratic actors in repressive environments is essential for countering the normalization of authoritarian digital governance.
Private companies must no longer operate in a legal and ethical vacuum. Regulatory mechanisms should ensure that firms exporting surveillance technologies are held accountable for complicity in human rights violations. Public pressure campaigns and state-level policy interventions—such as targeted sanctions or procurement restrictions—can help enforce these norms. At the same time, incentives should be offered for ethical innovation and secure technology development that supports open societies.
International cooperation among democracies must deepen through the sharing of intelligence, technologies, and best practices in countering cyber repression and disinformation. Cross-national partnerships can create rapid response frameworks to detect and disrupt strategic digital information operations. Capacity-building programs should support governments seeking to manage their digital ecosystems in ways that uphold civil liberties and protect against authoritarian creep.
Economic leverage should be strategically employed. Trade policies, investment frameworks, and development aid must be conditioned on adherence to digital rights standards. This includes shifting financial relationships away from authoritarian technology providers and toward partners committed to democratic norms. Financial institutions and donor agencies must integrate digital governance benchmarks into their programming.
Diplomacy should play a more assertive role in exposing and isolating regimes that abuse digital technologies. Bilateral engagements, international resolutions, and public diplomacy should be used to condemn repressive practices, promote digital transparency, and advocate for global standards of accountability. Countries like Egypt must be pressured to reform not only through external criticism but through coordinated global action that combines legal, economic, and diplomatic tools.
In conclusion, the diffusion of digital authoritarianism is a multi-dimensional and complex phenomenon driven by both state and corporate actors, operating through networks of learning, emulation, and cooperative interdependence. The Egyptian case exemplifies how these processes work in practice and the urgent need for a sustained, global response. Confronting this challenge will require a blend of regulation and resistance, innovation and accountability, diplomacy and solidarity. Only through such an approach can the digital realm be reclaimed as a space of freedom, rights, and democratic resilience.
Funding: This work was supported by the Gerda Henkel Foundation, AZ 01/TG/21, Emerging Digital Technologies and the Future of Democracy in the Muslim World.
Authors
Ihsan Yilmaz is Deputy Director (Research Development) of the Alfred Deakin Institute for Citizenship and Globalisation (ADI) at Deakin University, where he also serves as Chair in Islamic Studies and Research Professor of Political Science and International Relations. He previously held academic positions at the Universities of Oxford and London and has a strong track record of leading multi-site international research projects. His work at Deakin has been supported by major funding bodies, including the Australian Research Council (ARC), the Department of Veterans’ Affairs, the Victorian Government, and the Gerda Henkel Foundation.
(*) Ali Mamouri is a scholar and journalist specializing in political philosophy and theology. He is currently a Research Fellow at the Alfred Deakin Institute for Citizenship and Globalisation at Deakin University. With an academic background, Dr. Mamouri has held teaching positions at the University of Sydney, the University of Tehran, and Al-Mustansiriyah University, as well as other institutions in Iran and Iraq. He has also taught at the Qom and Najaf religious seminaries. From 2020 to 2022, he served as a Strategic Communications Advisor to the Iraqi Prime Minister, providing expertise on regional political dynamics. Dr. Mamouri also has an extensive career in journalism. From 2016 to 2023, he was the editor of Iraq Pulse at Al-Monitor, covering key political and religious developments in the Middle East. His work has been featured in BBC, ABC, The Conversation, Al-Monitor, and Al-Iraqia State Media, among other leading media platforms. As a respected policy analyst, his notable works include “The Dueling Ayatollahs: Khamenei, Sistani, and the Fight for the Soul of Shiite Islam” (Al-Monitor) and “Shia Leadership After Sistani” (Washington Institute). Beyond academia and journalism, Dr. Mamouri provides consultation to public and private organizations on Middle Eastern affairs. He has published several works in Arabic and Farsi, including a book on the political philosophy of Muhammad Baqir Al-Sadr and research on political Salafism. Additionally, he has contributed to The Great Islamic Encyclopedia and other major Islamic encyclopedias.
(**) Shahram Akbarzadeh is Convenor of Middle East Studies Forum (MESF) and Professor of International Politics, Deakin University (Australia). He held a prestigious ARC Future Fellowship (2013-2016) on the Role of Islam in Iran’s Foreign Policy-making and recently completed a Qatar Foundation project on Sectarianism in the Middle East. Professor Akbarzadeh has an extensive publication record and has contributed to the public debate on the political processes in the Middle East, regional rivalry and Islamic militancy. In 2022 he joined Middle East Council on Global Affairs as a Non-resident Senior Fellow.
(***) Muhammad Omer is a PhD student in political science at the Deakin University. His PhD is examining the causes, ideological foundations, and the discursive construction of multiple populisms in a single polity (Pakistan). His other research interests include transnational Islam, religious extremism, and vernacular security. He previously completed his bachelor’s in politics and history from the University of East Anglia, UK, and master’s in political science from the Vrije University Amsterdam.
References
Access Now. (2023). “مصر: جماعات حقوقية تدين الحجب الأخير لموقعين إخباريين –” https://www.accessnow.org/press-release/مصر-جماعات-حقوقية-تدين-الحجب-الأخير-لم/
Adler, Emanuel, and Vincent Pouliot. (2011). “International practices.” International theory 3(1): 1-36.
AFTE Egypt. (2020). “قائمة المواقع المحجوبة في مصر.” https://afteegypt.org/blocked-websites-list-ar
Ahmed, Zahid Shahab; Yilmaz, Ihsan; Akbarzadeh, Shahram & Bashirov, Galib. (2023). “Digital Authoritarianism and Activism for Digital Rights in Pakistan.” European Center for Populism Studies (ECPS). July 20, 2023. https://doi.org/10.55271/rp0042
Akbarzadeh, S.; Mamouri, A.; Bashirov, G., & Yilmaz, I. (2025). Social media, conspiracy theories, and authoritarianism: between bread and geopolitics in Egypt. Journal of Information Technology & Politics, 1–14. https://doi.org/10.1080/19331681.2025.2474000
Akbarzadeh, Shahram, Amin Naeni, Ihsan Yilmaz, and Galib Bashirov. (2024). “Cyber Surveillance and Digital Authoritarianism in Iran.” Global Policy, March 14, 2024.
https://www.globalpolicyjournal.com/blog/14/03/2024/cyber-surveillance-and-digital-authoritarianism-iran.
Al-Hathloul, Lina. (2022). “Dictators in Egypt and Saudi Arabia Love Smart Cities Projects — Here’s Why.” AccessNow. https://www.accessnow.org/smart-cities-projects/
Ambrosio, Thomas, and Jakob Tolstrup. (2019). “How Do We Tell Authoritarian Diffusion from Illusion? Exploring Methodological Issues of Qualitative Research on Authoritarian Diffusion.” Quality & Quantity 53(6): 2741-2763.
Ambrosio, Thomas. (2010). “Constructing a Framework of Authoritarian Diffusion: Concepts, Dynamics, and Future Research.” International Studies Perspectives 11(4): 375-392.
Amnesty International. (2020). “German-made FinSpy spyware found in Egypt, and Mac and Linux versions revealed.” https://www.amnesty.org/en/latest/research/2020/09/german-made-finspy-spyware-found-in-egypt-and-mac-and-linux-versions-revealed/
Anderson, Janna, and Lee Rainie. (2020). “Many Tech Experts Say Digital Disruption Will Hurt Democracy.” Pew Research Center. https://www.pewresearch.org/internet/2020/02/21/many-tech-experts-say-digital-disruption-will-hurt-democracy/
Appuhami, Ranjith; Perera, Sujatha and Perera, Hector. (2011). “Coercive policy diffusion in a developing country: The case of public-private partnerships in Sri Lanka.” Journal of Contemporary Asia 41(3): 431-451.
Arslan, Melike. (2022). “Legal Diffusion as Protectionism: The Case of the US Promotion of Antitrust laws.” Review of International Political Economy 1-24. https://doi.org/10.1080/09692290.2022.2158118
Atlantic Council. (2019). “The State of Emergency in Egypt: An Exception or Rule?” https://www.atlanticcouncil.org/blogs/menasource/the-state-of-emergency-in-egypt-an-exception-or-rule/
Bank, André. (2017). “The Study of Authoritarian Diffusion and Cooperation: Comparative Lessons on Interests Versus Ideology, Nowadays and in History.” Democratization 24(7): 1345-1357.
Barnett, Michael., and Finnemore, Martha. (2005). “The power of liberal international organizations.” Power in Global Governance 161: 163-171.
Bashirov, G.; Akbarzadeh, S.; Yilmaz, I. and Ahmed, Z. (2025). “Diffusion of Digital Authoritarian Practices in China’s Neighbourhood: The Cases of Iran and Pakistan.” Democratization, DOI: 10.1080/13510347.2025.2504588
Beissinger, Mark. (2007). “Structure and Example in Modular Political Phenomena: The Diffusion of Bulldozer, Rose, Orange and Tulip Revolutions.” Perspectives on Politics 5(2): 259–76.
Bendrath, Ralf, and Mueller, Milton. (2011). “The End of the Net as We Know It? Deep Packet Inspection and Internet Governance.” New Media & Society 13(7): 1142-1160.
Bergman, Ronen, and Walsh, Declan. (2019). “Egypt Is Using Apps to Track and Target Its Citizens, Report Says.” The New York Times. https://www.nytimes.com/2019/10/03/world/middleeast/egypt-cyber-attack-phones.html
Blaubach, Thomas. (2021). “Chinese Technology in the Middle East: A Threat to Sovereignty or an Economic Opportunity?” MEI Policy Center.
Bostrom, N. (2014). Superintelligence: Paths, Dangers, Strategies. New York: Oxford University Press.
Braun, Dietmar, and Gilardi, Fabrizio. (2006). “Taking ‘Galton’s Problem’ Seriously: Towards a Theory of Policy Diffusion.” Journal of theoretical politics 18(3): 298-322.
Breuer, Anita. (2012). “The Role of Social Media in Mobilizing Political Protest: Evidence from the Tunisian Revolution.” German Development Institute Discussion Paper 10: 1860-0441.
Cattle, Amy E. (2015). “Digital Tahrir Square: An Analysis of Human Rights and the Internet Examined through the Lens of the Egyptian Arab Spring.” Duke J. Comp. & Int’l L. 26: 417.
Damnjanović, I. (2015). “Polity without Politics? Artificial Intelligence versus Democracy: Lessons from Neal Asher’s Polity Universe.” Bulletin of Science, Technology & Society, 35(3-4), 76-83.
Day, Jones. (2022). “China Amends Anti-Monopoly Law: What You Need to Know.” Jones Day. https://www.jonesday.com/en/insights/2022/07/china-amends-antimonopoly-law
Deibert, Ronald, John Palfrey, Rafal Rohozinski, and Jonathan L. Zittrain. (2010). “Access Controlled: The Shaping of Power, Rights, and Rule in Cyberspace.” The MIT Press.
DFRLab. (2023). “Egyptian Twitter Network Amplifies Pro-Government Hashtags, Attacks Fact-checkers – DFRLab.” DFRLab. https://dfrlab.org/2023/03/23/egyptian-twitter-network-amplifies-pro-government-hashtags-attacks-fact-checkers/
Diamond, Larry, and Marc F. Plattner, eds. (2012). Liberation Technology: Social Media and the Struggle for Democracy. JHU Press.
Dobbin, Frank, Beth Simmons, and Geoffrey Garrett. (2007). “The Global Diffusion of Public Policies: Social Construction, Coercion, Competition, or Learning?” Annual Review of Sociology. 33: 449-472.
Dragu, Tiberiu, and Yonatan Lupu. (2021). “Digital Authoritarianism and the Future of Human Rights.” International Organization 75(4): 991-1017.
Durac, Vincent, and Francesco Cavatorta. (2022). Politics and Governance in the Middle East. Bloomsbury Publishing.
Egypt Today. (2022). “COP27: TMG, Schneider Partner to Provide Latest Smart Solutions, Sustainability Standards in Noor City.” Egypt Today. https://www.egypttoday.com/Article/6/120619/COP27-TMG-Schneider-partner-to-provide-latest-smart-solutions-sustainability
Elkins, Zachary, and Beth Simmons. (2005). “On waves, clusters, and diffusion: A conceptual framework.” The Annals of the American Academy of Political and Social Science 598(1): 33-51.
ECCHR (European Center for Constitutional and Human Rights). (2023). https://www.ecchr.eu/en/
Fatafta, Marwa. (2020). “Egypt’s new data protection law: data protection or data control?”. Access Now. https://www.accessnow.org/egypts-new-data-protection-law-data-protection-or-data-control/
Feldstein, Steven. (2019). The Global Expansion of AI Surveillance. Washington, DC: Carnegie Endowment for International Peace. https://carnegieendowment.org/2019/09/17/global-expansion-of-ai-surveillance-pub-79847
Feldstein, Steven. (2021). The Rise of Digital Repression: How Technology Is Reshaping Power, Politics, and Resistance. Oxford University Press.
Freedom House. (2021). “Freedom on the Net 2020 Report.” https://freedomhouse.org/sites/default/files/2020-10/10122020_FOTN2020_Complete_Report_FINAL.pdf accessed: 1/3/2021.
Freedom House (2022). “Egypt.” https://freedomhouse.org/country/egypt/freedom-net/2022.
Freedom House. (2022). “Freedom in the World.” https://freedomhouse.org/report/freedom-world
Freedom House. (2022). “Freedom on the Net.” https://freedomhouse.org/report/freedom-net
Gallagher, Ryan. (2022). “Sandvine Pulls Back from Russia as US, EU Tighten Control on Technology It Sells.” Bloomberg. https://www.bloomberg.com/news/articles/2022-06-03/sandvine-pulls-back-from-russia-as-us-eu-tighten-control-on-technology-it-sells
Gardels, Nathan, & Berggruen, Nicolas. (2019). Renovating Democracy: Governing in the Age of Globalization and Digital Capitalism. Berkeley: University of California Press.
Geere, Duncan. 2012. “How Deep Packet Inspection Works.” Wired. https://www.wired.co.uk/article/how-deep-packet-inspection-works
Gilardi, Fabrizio. (2010). “Who learns from what in policy diffusion processes?” American Journal of Political Science.54(3): 650-666.
Gilardi, Fabrizio. (2012). “Transnational Diffusion: Norms, Ideas, and Policies.” Handbook of International Relations. 2: 453-477.
Golomshtok, Igor. (1990). Totalitarian Art in the Soviet Union, the Third Reich, Fascist Italy, and the People’s Republic of China. https://ci.nii.ac.jp/ncid/BA21226005
Helbing, Dirk., et al. (2019). “Will Democracy Survive Big Data and Artificial Intelligence?” Scientific American. https://www.scientificamerican.com/article/will-democracy-survive-big-data-and-artificial-intelligence/
Hellmeier, Sebastian. (2016). “The dictator’s digital toolkit: Explaining Variation in Internet Filtering in Authoritarian Regimes.” Politics & Policy. 44(6): 1158-1191.
Hernández, Marianne Díaz, Felicia Anthonio, Sage Cheng, and Alexia Skok. (2023). “Internet Shutdowns in 2021: The Return of Digital Authoritarianism.” Access Now. https://www.accessnow.org/internet-shutdowns-2021/
Hillman, Jonathan E. (2021). The Digital Silk Road: China’s Quest to Wire the World and Win the Future. Profile Books.
Hillman, Jonathan E, and Maesea McCalpin. (2019). “Watching Huawei’s safe cities”. Center for Strategic and International Studies (CSIS).
Hong, Caylee. (2022). “Safe Cities in Pakistan: Knowledge Infrastructures, Urban Planning, and the Security State.” Antipode 54(5): 1476-1496.
Human Rights Watch. (2017). “We Do Unreasonable Things Here’ Torture and National Security in al-Sisi’s Egypt.” https://www.hrw.org/sites/default/files/report_pdf/egypt0917_web.pdf.
Julien, Giry and Doğan Gürpınar. (2020). “Functions and uses of conspiracy theories in authoritarian regimes.” In: Routledge Handbook of Conspiracy Theories.
Kerr, Jaclyn A. (2018). “Authoritarian Practices in the Digital Age| Information, Security, and Authoritarian Stability: Internet Policy Diffusion and Coordination in the Former Soviet Region.” International Journal of Communication 12: 21.
Khalil, Lydia. (2020). “Digital authoritarianism, China and COVID.” Lowy Institute.
Koesel, Karrie J., and Valerie J. Bunce. (2013). “Diffusion-proofing: Russian and Chinese Responses to Waves of Popular Mobilizations Against Authoritarian Rulers.” Perspectives on Politics. 11(3): 753-768.
Kurlantzick, Joshua. (2020). “China’s Digital Silk Road Initiative: A Boon for Developing Countries or a Danger to Freedom?” The Diplomat. https://thediplomat.com/2020/12/chinas-digital-silk-road-initiative-a-boon-for-developing-countries-or-a-danger-to-freedom
Kynge, James, Valerie Hopkins, Helen Warrell, and Kathrin Hille. (2021). “Exporting Chinese Surveillance: The Security Risks of ‘Smart Cities’.” Financial Times. https://www.ft.com/content/76fdac7c-7076-47a4-bcb0-7e75af0aadab
Laskai, Lorand. (2019). “How China Is Supplying Surveillance Technology and Training Around the World.” Privacy International.
Lilkov, Dimitar. (2020). “Made in China: Tackling Digital Authoritarianism.” European View 19(1): 110-110.
Malena, Jorge. (2021). “The extension of the digital silk road to Latin America: Advantages and potential risks.” Brazilian Center for International Relations.
Marczak, Bill, Jakub Dalek, Sarah McKune, Adam Senft, John Scott-Railton, and Ron Deibert. (2018). “Bad Traffic: Sandvine’s PacketLogic Devices Used to Deploy Government Spyware in Turkey and Redirect Egyptian Users to Affiliate Ads?” The Citizen Lab. https://citizenlab.ca/2018/03/bad-traffic-sandvines-packetlogic-devices-deploy-government-spyware-turkey-syria/
Marczak, Bill., et al. (2018). “Bad Traffic: Sandvine’s Packet Logic Devices Used to Deploy Government Spyware in Turkey and Redirect Egyptian Users to Affiliate Ads?” The Citizen Lab. https://citizenlab.ca/2018/03/bad-traffic-sandvines-packetlogic-devices-deploy-government-spyware-turkey-syria/
Mare, Admire. (2020). “Internet Shutdowns in Africa| State-Ordered Internet Shutdowns and Digital Authoritarianism in Zimbabwe.” International Journal of Communication, 14, 20.
Mansgurat. (2018). “قانون مكافحة جرائم تقنية المعلومات.” Manshurat. https://doi.org/https://manshurat.org/node/31487.
Menshawy, Mustafa. (2021). “Why Is Egypt Building a New Capital?” Al-Jazeera.https://www.aljazeera.com/opinions/2021/7/5/why-is-egypt-building-a-new-capital.
Michaelsen, Marcus. (2018). “Transforming Threats to Power: The International Politics of Authoritarian Internet Control in Iran.” International Journal of Communication. 12: 3856-3876.
Mir, Asfandyar, Tamar Mitts and Paul Staniland. (2022). “Political Coalitions and Social Media: Evidence from Pakistan.” Perspectives on Politics, 1-20.
Mourad, Mahmoud and Aidan Lewis. (2021). “From creaking Cairo, Egypt Plans High-tech Leap with New Capital.” Reuters. https://www.reuters.com/world/middle-east/creaking-cairo-egypt-plans-high-tech-leap-with-new-capital-2021-09-02/.
Muggah, Robert. (2021). “Digital Privacy Comes at a Price.” Agenda. https://www.weforum.org/agenda/2021/09/how-to-protect-digital-privacy
Polyakova, A., & Meserole, C. (2019). “Exporting digital authoritarianism: The Russian and Chinese models.” Policy Brief, Democracy and Disorder Series, Brookings, 1-22.
Privacy International. (2019). “State of Privacy Egypt.” https://privacyinternational.org/state-privacy/1001/state-privacy-egypt.
Radavoi, C. N. (2019). “The Impact of Artificial Intelligence on Freedom, Rationality, Rule of Law and Democracy: Should We Not Be Debating It?” Texas Journal on Civil Liberties & Civil Rights, 25, 107.
Rezk, Farida, and Mohamed Hashish. (2023). “In Brief: Telecoms Regulation in Egypt.” Lexology. https://www.lexology.com/library/detail.aspx?g=85c424f1-84bb-4288-8d48-df69c913cbc9#:~:text=The%20Telecom%20Law%20was%20amended,a%20permit%20from%20the%20relevant.
Roberts, Margaret. (2018). Censored: Distraction and Diversion Inside China’s Great Firewall. Princeton: Princeton University Press.
Routledge Handbook of Conspiracy Theories. (2020). Routledge eBooks. https://doi.org/10.4324/9780429452734
Rogers, Everett M. (2010). Diffusion of innovations. Simon and Schuster.
RSF. (2018). “Egypt’s New Cybercrime Law Legalizes Internet Censorship.” https://rsf.org/en/egypt-s-new-cybercrime-law-legalizes-internet-censorship.
Ruijgrok, Kris. (2017). “From the Web to the Streets: Internet and Protests Under Authoritarian Regimes.” Democratization. 24(3): 498-520.
Ryan-Mosley, Tate. (2022). “The world is moving closer to a new cold war fought with authoritarian tech.” MIT Technology Review. https://www.technologyreview.com/2022/09/22/1059823/cold-war-authoritarian-tech-china-iran-sco/?truid=%2A%7CLINKID%7C%2A
Scott-Railton, John, Bill Marczak, Ramy Raoof, and Etienne Maynier. (2017). “Nile Phish: Large-Scale Phishing Campaign Targeting Egyptian Civil Society.” The Citizen Lab. https://citizenlab.ca/2017/02/nilephish-report
Social Media Exchange (SMEX). (2018). “In Egypt’s Sinai Peninsula, Network Shutdowns Leave Civilians Unreachable — and Unable to Call for Help.” Global Voices. February 14, 2018. https://globalvoices.org/2018/02/14/in-egypts-sinai-peninsula-network-shutdowns-leave-civilians-unreachable-and-unable-to-call-for-help/.
Statista. (2024). “Egypt: Number of Internet Users.” https://www.statista.com/statistics/462957/internet-users-egypt/
Stepan, Alfred, eds. (2018). Democratic transition in the Muslim world: a global perspective (Vol. 35). Columbia University Press.
Stone, P., et al. (2016). One Hundred Year Study on Artificial Intelligence: Report of the 2015-2016 Study Panel. Stanford: Stanford University Press. http://ai100.stanford.edu/2016-report.
Strang, David. (1991). “Adding Social Structure to Diffusion Models: An Event History Framework.” Sociological Methods & Research 19(3): 324-353.
Tang, Min. (2020). “Huawei Versus the United States? The Geopolitics of Exterritorial Internet Infrastructure.” International Journal of Communication. 14, 22.
Taylor, Monique. (2022). “China’s Digital Authoritarianism Goes Global.” In: China’s Digital Authoritarianism: A Governance Perspective, pp. 111-130. Cham: Springer International Publishing.
Teets, Jessica C, and William Hurst. (2014). “Introduction: The Politics and Patterns of Policy Diffusion in China.” In: Local Governance Innovation in China, pp. 1-24. Routledge.
Triolo, Paul. (2020). “The Digital Silk Road: Expanding China’s Digital Footprint.” Eurasia Group. https://www.eurasiagroup.net/files/upload/Digital-Silk-Road-Expanding-China-Digital-Footprint.pdf.
Weber, Valentin. (2019). “The Worldwide Web of Chinese and Russian Information Controls.” Center for Technology and Global Affairs, University of Oxford.
Welle, Deutsche. (2005). “مدونة ‘دلو معلومات منال وعلاء’ تفوز بجائزة منظمة مراسلون بلا حدود.” dw.com.https://www.dw.com/ar/%D9%85%D8%AF%D9%88%D9%86%D8%A9-%D8%AF%D9%84%D9%88-%D9%85%D8%B9%D9%84%D9%88%D9%85%D8%A7%D8%AA-%D9%85%D9%86%D8%A7%D9%84-%D9%88%D8%B9%D9%84%D8%A7%D8%A1-%D8%AA%D9%81%D9%88%D8%B2-%D8%A8%D8%AC%D8%A7%D8%A6%D8%B2%D8%A9-%D9%85%D9%86%D8%B8%D9%85%D8%A9-%D9%85%D8%B1%D8%A7%D8%B3%D9%84%D9%88%D9%86-%D8%A8%D9%84%D8%A7-%D8%AD%D8%AF%D9%88%D8%AF/a-1774501.
Welle, Deutsche. (2023). “إحالة 3 صحفيات في ‘مدى مصر’ للمحاكمة.” dw.com. https://www.dw.com/ar/%D8%A5%D8%AD%D8%A7%D9%84%D8%A9-3-%D8%B5%D8%AD%D9%81%D9%8A%D8%A7%D8%AA-%D9%81%D9%8A-%D9%85%D8%AF%D9%89-%D9%85%D8%B5%D8%B1-%D9%84%D9%84%D9%85%D8%AD%D8%A7%D9%83%D9%85%D8%A9-%D8%A8%D8%B9%D8%AF-%D8%AA%D8%AD%D9%82%D9%8A%D9%82-%D8%B9%D9%86-%D9%85%D8%AE%D8%A7%D9%84%D9%81%D8%A7%D8%AA-%D9%85%D8%A7%D9%84%D9%8A%D8%A9-%D9%84%D8%A8%D8%B1%D9%84%D9%85%D8%A7%D9%86%D9%8A%D9%8A%D9%86/a-64851329.
Wheeler, Deborah. (2017). Digital Resistance in the Middle East: New Media Activism in Everyday Life. Edinburgh: Edinburgh University Press.
Worldometer. (2024). https://www.worldometers.info/world-population/egypt-population/.
x.com. n.d. X (Formerly Twitter). https://x.com/hrw/status/1719008193366700294.
Xu, Xu. (2021). “To Repress or to Co‐opt? Authoritarian Control in the Age of Digital Surveillance.” American Journal of Political Science 65(2): 309-325.
Yan, Yau Tsz. (2019). “Smart Cities or Surveillance? Huawei in Central Asia.” The Diplomat. https://thediplomat.com/2019/08/smart-cities-or-surveillance-huawei-in-central-asia.
Yenigun, Halil Ibrahim. (2021). “Turkey as a Model of Muslim Authoritarianism?” In: Routledge Handbook of Illiberalism, pp. 840-857. Routledge.
Yilmaz, Ihsan; Shahram Akbarzadeh, and Galib Bashirov. (2023). “Strategic Digital
Information Operations (SDIOs).” Populism & Politics (P&P). European Center for
Populism Studies (ECPS).
Yilmaz, I.; Akbarzadeh, S.; Abbasov, N. & Bashirov, G. (2024). “The Double-Edged Sword: Political Engagement on Social Media and Its Impact on Democracy Support in Authoritarian Regimes.” Political Research Quarterly, 0(0). https://doi.org/10.1177/10659129241305035
Yilmaz, I. and K. Shakil. (2025). Reception of Soft and Sharp Powers: Turkey’s Civilisationist Populist TV Dramas in Pakistan. Singapore: Palgrave Macmillan.
Yilmaz, I.; Morieson, N., & Shakil, K. (2025). “Authoritarian diffusion and sharp power through TV dramas: resonance of Turkey’s ‘Resurrection: Ertuğrul’ in Pakistan.” Contemporary Politics, 1–21.https://doi.org/10.1080/13569775.2024.2447138
Zhang, Wenxian; Ilan Alon, and Christoph Lattemann, eds. (2020). Huawei Goes Global: Volume I: Made in China for the World. Springer International Publishing.
Ziccardi, Giovanni. (2012). Resistance, Liberation Technology and Human Rights in the Digital Age, vol. 7. Springer Science & Business Media.